Proteogenomics in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma reveals new biological fingerprint of cerebral small vessel disease
- PMID: 41266628
- PMCID: PMC12705447
- DOI: 10.1038/s43587-025-01006-w
Proteogenomics in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma reveals new biological fingerprint of cerebral small vessel disease
Abstract
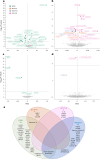
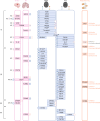
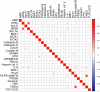
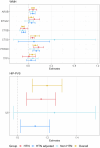
Cerebral small vessel disease (cSVD) is a leading cause of stroke and dementia with no specific treatment, of which molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. To identify potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets, we applied Mendelian randomization to examine over 2,500 proteins measured in plasma and, uniquely, cerebrospinal fluid, in relation to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) markers of cSVD in more than 40,000 individuals. Here we show that 49 proteins are associated with MRI markers of cSVD, most prominently in cerebrospinal fluid. We highlight associations that are consistent across platforms and ancestries, and supported by complementary observational analyses, and we explore differences between fluids. The proteins are enriched in pathways related to the extracellular matrix, immune response and microglial activity. Many also associate with stroke and dementia, and several correspond to existing drug targets. Together, these findings reveal a robust biological fingerprint of cSVD and highlight opportunities for biomarker and drug discovery and repositioning.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: C.C. has received research support from GSK and EISAI and is a member of the advisory board of Circular Genomics and owns stocks in this company. C.C. is part of the scientific advisory board for ADmit. B.P. serves on the Steering Committee of the Yale Open Data Project funded by Johnson & Johnson. C.C. is a member of the scientific advisory board of Circular Genomics and owns stocks, and is on the scientific advisory board of ADmit and Alamar. C.C. consults for Sanofi, Novo Nordisk and Owkin. C.C. has received research support from GSK, Danaher and EISAI. P.M.M. has received an honorarium as Chair of the UKRI Medical Research Council Neuroscience and Mental Health Board until March 2024. P.M.M. acknowledges consultancy fees from Biogen, Sudo, Nimbus and GSK. P.M.M. has received speakers’ honoraria from Sanofi and Redburn, and has received research or educational funds from Biogen, Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb and Nimbus. J.M.W. declares no commercial competing interests, is in receipt of various academic research grants and is chief investigator for LACunar Intervention Trials. The authors declare no competing interests with respect to research, authorship and/or publication of this article. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures











Update of
-
Proteogenomics in cerebrospinal fluid and plasma reveals new biological fingerprint of cerebral small vessel disease.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 2:rs.3.rs-4535534. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4535534/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Nat Aging. 2025 Dec;5(12):2514-2531. doi: 10.1038/s43587-025-01006-w. PMID: 39011113 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AG066444/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL120393/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG059421/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG003991/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 75N92021D00006/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL103612/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- ANR-18-RHUS-0002, ANR-10-COHO-05/Agence Nationale de la Recherche (French National Research Agency)
- U01 AG058922/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG044546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG053303/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL130114/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG026276/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG058501/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087652/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS129032/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG074007/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG063507/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201800001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL172803/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066546/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG062723/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01NS129032/U.S. Department of Health Human Services | NIH | Center for Information Technology (Center for Information Technology, National Institutes of Health)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

