Breakthroughs and Opportunities of Biopolymer Coatings: A Bibliometric Analysis on Their Future Prospects for the Sustainable Food Packaging Industry
- PMID: 41267751
- PMCID: PMC12629704
- DOI: 10.1155/tswj/5337593
Breakthroughs and Opportunities of Biopolymer Coatings: A Bibliometric Analysis on Their Future Prospects for the Sustainable Food Packaging Industry
Abstract
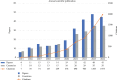
Plastic packaging poses significant environmental challenges due to its resistance to natural degradation. In response, there has been a growing body of research dedicated to developing sustainable packaging alternatives, particularly those based on biodegradable materials. Biopolymer-based packaging is widely recognized for its enhanced environmental compatibility, owing to its capacity for natural decomposition and reduced ecological footprint. This study presents a comprehensive bibliometric analysis of recent advancements in biopolymer coatings for food packaging, with a focus on their potential to enhance food safety, quality, and shelf life. Analysis of publications from 2015 to 2024 indicates a substantial and consistent rise in scholarly output related to biopolymer-based packaging solutions, driven by global efforts to mitigate plastic waste and its associated environmental impacts. The findings suggest that the future trajectory of biodegradable packaging research should emphasize the development of materials that simultaneously support human health and environmental sustainability. Bibliometric mapping identified polylactic acid (PLA), polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), chitosan, and cellulose-based polymers as key areas of innovation, highlighting their increasing prominence and interdisciplinary research significance. These materials are notable for their biodegradability, and many also exhibit intrinsic functional properties such as antimicrobial and antioxidant activities-attributes that are highly desirable in food packaging applications. Biopolymer coatings, in particular, have demonstrated excellent barrier properties, including controlled permeability to moisture and oxygen, which are critical for maintaining food integrity. Such coatings contribute to extended shelf life by minimizing dehydration and oxidative damage while concurrently offering protection against microbial contamination. Despite the promising functional characteristics of these materials, several challenges continue to hinder their widespread adoption. Key barriers include high production costs, the limited availability of industrial composting infrastructure, and the general lack of consumer awareness regarding appropriate disposal practices. Addressing these challenges will require coordinated efforts across research, industry, and policy domains. To enable scalable implementation, future innovation must achieve critical advancements in materials science, biopolymer production efficiency, and regulatory alignment. A comprehensive, multidisciplinary approach will be essential to realize the full potential of biopolymer coatings as sustainable alternatives to conventional plastic packaging.
Keywords: bibliometric analysis; biodegradable packaging; biopolymer coating; environmental sustainability; food preservation; global research trends.
Copyright © 2025 Huda Mohamad Elmatsani et al. The Scientific World Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Mariana M., Alfatah T., Abdul Khalil H. P. S., et al. A Current Advancement on the Role of Lignin as Sustainable Reinforcement Material in Biopolymeric Blends. Journal of Materials Research and Technology . 2021;15:2287–2316. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.08.139. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

