High expression of interleukin-18 receptor alpha correlates with severe respiratory viral disease and defines T cells with reduced cytotoxic signatures
- PMID: 41285788
- PMCID: PMC12644894
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-65262-5
High expression of interleukin-18 receptor alpha correlates with severe respiratory viral disease and defines T cells with reduced cytotoxic signatures
Abstract
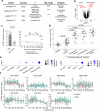
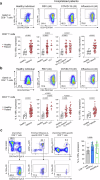
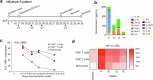
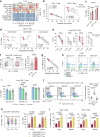
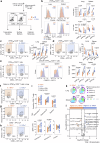
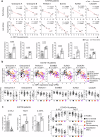
Hyperactivated immunity underpins severe outcomes of respiratory viral infections, yet specific immune perturbations are ill-defined. Our recent findings identified OLAH (oleoyl-ACP-hydrolase) as a driver of life-threatening viral diseases. In the same patient cohorts, we now identify the gene encoding IL-18Rα chain (IL18R1), as being highly expressed in life-threatening influenza, COVID-19, RSV and multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) and demonstrate markedly elevated surface protein IL-18Rα expression on CD8 T cells in these infections. Using a mouse model of severe influenza, we further show that high IL-18Rα expression on effector T cells is associated with increased disease severity. We find that IL-18Rα expression on CD8 T cells is inversely associated with cytotoxicity-related genes, including granzyme A, granzyme B, perforin, Eomes, and KLRG-1. Our study demonstrates that IL-18Rα is associated with severe and fatal respiratory disease outcomes and proposes the use of IL-18Rα as a potential biomarker for severe respiratory viral disease.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: HAM and BYC consult for Ena Respiratory. AGR received research support from Illumina. PGT is on the SAB of Immunoscape and Cytoagents; consulted for JNJ, received travel support/honoraria from Illumina, 10X Genomics, has patents related to TCR discovery. JCC, PGT have patents related to treating or reducing the severity of viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Nguyen, T. H. O., Rowntree, L. C., Chua, B. Y., Thwaites, R. S. & Kedzierska, K. Defining the balance between optimal immunity and immunopathology in influenza virus infection. Nat. Rev. Immunol.24, 720–735 (2024). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

