Tobacco Smoke Exposure and Oxidative Stress: The Role of Circulating Lipopolysaccharides in Heated and Conventional Products
- PMID: 41300474
- PMCID: PMC12649242
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox14111316
Tobacco Smoke Exposure and Oxidative Stress: The Role of Circulating Lipopolysaccharides in Heated and Conventional Products
Abstract
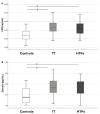
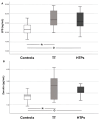
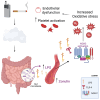
Background: Exposure to tobacco smoke, from conventional tobacco cigarettes (CTC) or heated tobacco products (HTPs), increases oxidative stress, causing endothelial dysfunction and higher cardiovascular risk. It is unclear whether smoke exposure also promotes low-grade endotoxemia, potentially activating NADPH oxidase and further impairing endothelial function. This study assessed serum lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels in children and adults actively or passively exposed to conventional cigarette smoke or HTPs, compared with non-exposed controls. Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study comprising 26 children passively exposed to HTPs, 26 children exposed to CTC, and 26 unexposed controls, as well as 20 adult chronic HTP users, 20 chronic CTC, and 20 non-smoking adults. Circulating LPS was measured alongside oxidative stress markers (NOX2, H2O2), endothelial function, intestinal permeability (zonulin), and nicotine exposure (serum cotinine). Results: Exposed children had higher cotinine, LPS, and zonulin than controls, with no differences between HTP and CTC groups. Multiple linear regression analysis identified cotinine (β = 0.343; p = 0.005) and zonulin (β = 0.441; p < 0.001) as independent LPS predictors. In adults, LPS and zonulin were higher in both smoker groups versus controls; zonulin (β = 0.477; p < 0.001) and nitric oxide bioavailability (β = -0.307; p = 0.007) independently predicted LPS. Conclusions: Passive and active exposure to CTC or HTPs increases low-grade endotoxemia and zonulin, potentially driving NOX2-mediated oxidative stress.
Keywords: LPS; NADPH-oxidase 2; NOX-2; atherosclerosis; cigarettes; endothelial dysfunction; flow-mediated dilation; heated tobacco products; lipopolysaccharides; smoking.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Magna A., Polisena N., Polisena L., Bagnato C., Pacella E., Carnevale R., Nocella C., Loffredo L. The Hidden Dangers: E-Cigarettes, Heated Tobacco, and Their Impact on Oxidative Stress and Atherosclerosis-A Systematic Review and Narrative Synthesis of the Evidence. Antioxidants. 2024;13:1395. doi: 10.3390/antiox13111395. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

