Artificial Intelligence-Based Evaluation of Post-Procedural Electrocardiographic Parameters to Identify Patients at Risk of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Transcatheter Ablation
- PMID: 41303280
- PMCID: PMC12653835
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm14228248
Artificial Intelligence-Based Evaluation of Post-Procedural Electrocardiographic Parameters to Identify Patients at Risk of Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence After Transcatheter Ablation
Abstract
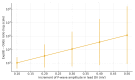
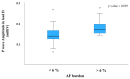
Background/Objectives: Arrhythmic recurrence is a common issue affecting a significant percentage of patients undergoing transcatheter ablation (TCA) of Atrial Fibrillation (AF). The use of artificial intelligence (AI) for the identification of electrocardiographic predictors of post-ablation recurrence may offer a valuable and cost-effective approach to improve risk stratification and optimize follow-up. This study aims to investigate the relationship between post-procedural electrocardiographic (ECG) P-wave parameters, measured using AI, and AF recurrence in patients undergoing transcatheter ablation (TCA). Methods: Seventy-four patients (age 62.36 ± 10.4 years) with a diagnosis of AF were retrospectively analyzed. ECGs were processed using AI software to analyze P-wave-related variables. All patients had either an implantable loop recorder (ILR) or another form of cardiac implantable electronic device (CIED). Results: Post-procedural P-wave amplitude in lead II (PwA in lead II) showed a significant association with AF recurrence, defined as an average arrhythmic burden >6% at one-year follow-up. Conclusions: These findings underscore the potential of PwA in lead II as a biomarker for the follow-up of patients undergoing TCA and highlight the contribution of AI in the analysis of electrocardiographic parameters predictive of AF recurrence. Together, these results may contribute to the development of early risk-stratification strategies following catheter ablation.
Keywords: P-wave; artificial intelligence; atrial fibrillation; catheter ablation; electrocardiography; recurrence prediction; risk stratification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- D’Ascenzo F., Corleto A., Biondi-Zoccai G., Anselmino M., Ferraris F., Di Biase L., Natale A., Hunter R.J., Schilling R.J., Miyazaki S., et al. Which Are the Most Reliable Predictors of Recurrence of Atrial Fibrillation after Transcatheter Ablation?: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013;167:1984–1989. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2012.05.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Intzes S., Zagoridis K., Symeonidou M., Spanoudakis E., Arya A., Dinov B., Dagres N., Hindricks G., Bollmann A., Kanoupakis E., et al. P-Wave Duration and Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence after Catheter Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Europace. 2023;25:450–459. doi: 10.1093/europace/euac210. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources