Predictive Fermentation Control of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Using Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks
- PMID: 41304285
- PMCID: PMC12654792
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms13112601
Predictive Fermentation Control of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum Using Deep Learning Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
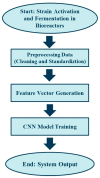
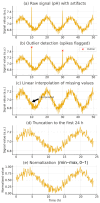
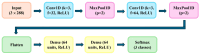
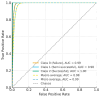
The fermentation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum is a complex bioprocess due to the nonlinear and dynamic nature of microbial growth. Traditional monitoring methods often fail to provide early and actionable insights into fermentation outcomes. This study proposes a deep learning-based predictive system using convolutional neural networks (CNNs) to classify fermentation trajectories and anticipate final cell counts based on the first 24 h of process data. A total of 52 fermentation runs were conducted, during which real-time parameters, including pH, temperature, and dissolved oxygen, were continuously recorded and transformed into time-series feature vectors. After rigorous preprocessing and feature selection, the CNN was trained to classify fermentation outcomes into three categories: successful, semi-successful, and failed batches. The model achieved a classification accuracy of 97.87%, outperforming benchmark models such as LSTM and XGBoost. Validation experiments demonstrated the model's practical utility: early predictions enabled timely manual interventions that effectively prevented batch failures or improved suboptimal fermentations. These findings suggest that deep learning provides a robust and scalable framework for real-time fermentation control, with significant implications for enhancing efficiency and reducing costs in industrial probiotic production.
Keywords: Lactiplantibacillus plantarum; bioprocess control; convolutional neural network; deep learning; fermentation prediction; probiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Research Nester . Microbial Fermentation Technology Market Size & Share, by Application (Antibiotics, Probiotics Supplements, Monoclonal Antibodies, Recombinant Proteins, Biosimilars, Vaccines, Enzymes, Small Molecules); End-User (Bio-Pharmaceutical Companies, Contract Research Organizations (CROS), CMOs & CDMOs, Academic & Research Institutes); Type (Medical, Industrial, Alcohol Beverages, Food and Feed Products)—Global Supply & Demand Analysis, Growth Forecasts, Statistics Report 2025–2037. Research Nester; Noida, India: 2024. Report ID: 5329.
-
- Sharma R., Garg P., Kumar P., Bhatia S.K., Kulshrestha S. Microbial fermentation and its role in quality improvement of fermented foods. Fermentation. 2020;6:106. doi: 10.3390/fermentation6040106. - DOI
-
- Stanbury P.F. Fermentation technology. Mol. Biol. Biotechnol. 2000;1:1–24.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

