Saliva-driven surface-engineered Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron alleviates hypertension
- PMID: 41312226
- PMCID: PMC12648485
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.11.007
Saliva-driven surface-engineered Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron alleviates hypertension
Abstract
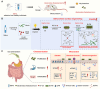
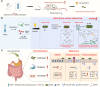
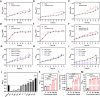
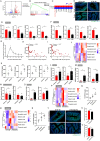
Oral environment is closely linked to blood pressure regulation. However, the underlying mechanisms remain poorly understood, and strategies for harnessing this relationship to modulate blood pressure are still scarce. Saliva, abundant in the oral cavity, was demonstrated to play a critical role in sustaining the abundance of gut Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron (Bt), contributing to blood pressure reduction. Metal ions and mucins in saliva were further identified as factors responsible for Bt growth. Building on this discovery, we developed a saliva-inspired, surface-engineered Bt (Bt-FM) that reconstructs the cooperative microenvironment formed by metal ions and mucins in natural saliva. The biomimetic Fe2+-chitosan-mucin (FM) layer recapitulates both the protective and regulatory features of saliva, enabling Bt to maintain structural integrity and metabolic activity under gastrointestinal stress. This design transforms salivary cues into a functional engineering strategy that enhances Bt stability, colonization, and antihypertensive efficacy in vivo. Further exploration revealed that anti-hypertensive effects involve synthesizing short-chain fatty acids, modulating sodium ion channels, and maintaining gut immune homeostasis. This work pioneers a dynamic, material-based platform to probiotic enhancement for hypertension management.
Keywords: Hypertension; Probiotic; Saliva; Surface-engineering; gut microbiota.
© 2025 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Xie X., Atkins E., Lv J., Bennett A., Neal B., Ninomiya T., Woodward M., MacMahon S., Turnbull F., Hillis G.S., Chalmers J., Mant J., Salam A., Rahimi K., Perkovic V., Rodgers A. Effects of intensive blood pressure lowering on cardiovascular and renal outcomes: updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. 2016;387(10017):435–443. - PubMed
-
- Endres M., Heuschmann P.U., Laufs U., Hakim A.M. Primary prevention of stroke: blood pressure, lipids, and heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2011;32(5):545–552. - PubMed
-
- Miller J.B., Hrabec D., Krishnamoorthy V., Kinni H., Brook R.D. Evaluation and management of hypertensive emergency. Br. Med. J. 2024;386 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

