Distributional bias compromises leave-one-out cross-validation
- PMID: 41313770
- PMCID: PMC12662204
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adx6976
Distributional bias compromises leave-one-out cross-validation
Abstract
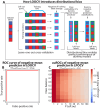
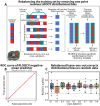
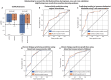
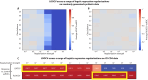
Cross-validation is a common method for evaluating machine learning models. "Leave-one-out cross-validation," in which each data instance is used to test a model trained on all other instances, is often used in data-scarce regimes. As common metrics such as the R2 score cannot be calculated for a single prediction, predictions are commonly aggregated across folds for performance evaluation. Here, we prove that this creates "distributional bias": a negative correlation between the average label of each training fold and the label of its corresponding test instance. As machine learning models tend to regress to the mean of their training data, this bias tends to negatively affect performance evaluation and hyperparameter optimization. We demonstrate that distributional bias exists across diverse tasks, models, and evaluation approaches, and can bias against stronger regularization. To address it, we developed a generalizable rebalanced cross-validation that is robust to distributional bias in both classification and regression, and demonstrates improved performance in simulations, machine learning benchmarks, and several published analyses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Distributional bias compromises leave-one-out cross-validation.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2025 Mar 24:arXiv:2406.01652v2. ArXiv. 2025. Update in: Sci Adv. 2025 Nov 28;11(48):eadx6976. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adx6976. PMID: 38883233 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Boyce M. S., Vernier P. R., Nielsen S. E., Schmiegelow F. K. A., Evaluating resource selection functions. Ecol. Model. 157, 281–300 (2002).
-
- Liu Y., Han T., Ma S., Zhang J., Yang Y., Tian J., He H., Li A., He M., Liu Z., Wu Z., Zhao L., Zhu D., Li X., Qiang N., Shen D., Liu T., Ge B., Summary of ChatGPT-Related research and perspective towards the future of large language models. Meta Radiol. 1, 100017 (2023).
-
- K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, J. Sun, Deep residual learning for image recognition. arXiv:1512.03385 [cs.CV] (2015).
-
- O. P. Jena, B. Bhushan, N. Rakesh, P. N. Astya, Y. Farhaoui, Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Efficacy Improvement of Healthcare Systems (CRC Press, 2022).
-
- Lecun Y., Bottou L., Bengio Y., Haffner P., Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 86, 2278–2324 (1998).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

