Tunable optoelectronic properties of reduced graphene oxide superlattices intercalated with poly(2-amino-1-mercaptobenzene) for Van der Waals photonic heterostructures
- PMID: 41318719
- PMCID: PMC12669602
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-19956-x
Tunable optoelectronic properties of reduced graphene oxide superlattices intercalated with poly(2-amino-1-mercaptobenzene) for Van der Waals photonic heterostructures
Abstract
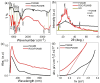
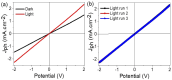
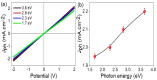
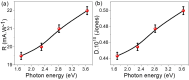
We have discovered a novel class of van der Waals (vdW) materials composed of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) superlattices that can be intercalated with various polymeric compounds. The bandgap in these groundbreaking graphene oxide-derived materials can be modulated and set by altering the reduced oxygen concentration and varying the intercalating agent's quantity. As such, these vdW materials could possess superior electro-optical features and a broader scope of applications than traditional graphene. For clarity on this concept, we outline the synthesis of these materials. We have successfully produced them and confirmed their exceptional optoelectronic characteristics through measurement. For instance, we intercalated highly ordered layers of rGO using poly-2-amino-1-mercaptobenzene (P2AMB) as an exemplary case. The resulting novel vdW material demonstrated extraordinary optical broadband absorbance up to 690 nm due to its fine crystalline size of 16 nm and a small bandgap of 1.86 eV, which is further tunable by decreasing the oxygen concentration in the graphene oxide sheets. We tested this vdW thin film as a light-capturing optoelectronic device under various photon energies. The device generated a high current density (Jph) of up to 2.2 mA/cm² and a photoresponsivity (R) of up to 22.0 mA/W, demonstrating its high sensitivity and technical advantages. This vdW material can be quickly and cheaply produced in large quantities, making it a promising option for light-capturing applications.
Keywords: Light sensor; Optoelectronic; Photon capture; Poly-2-amino-1-mercaptobenzene; Reduced graphene oxide.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Ethical approval: This study does not include any humans or animal studies.
Figures



References
-
- Kwon, J. H. & Choi, K. C. Highly reliable and stretchable OLEDs based on facile patterning method: toward stretchable organic optoelectronic devices. Npj Flex. Electron.8, 17 (2024).
-
- Patel, A. B. et al. Transferrable thin film of ultrasonically exfoliated MoSe2 nanocrystals for efficient visible-light photodetector. Phys. E: Low-dimensional Syst. Nanostruct.119, 114019 (2020).
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

