Functional Outcomes and Complications of Non-surgical Management for Midshaft Clavicle Fractures
- PMID: 41328111
- PMCID: PMC12665380
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.95788
Functional Outcomes and Complications of Non-surgical Management for Midshaft Clavicle Fractures
Abstract
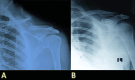
Introduction Midshaft clavicle fractures are commonly managed conservatively, especially in resource-limited settings. While union rates are generally high, concerns remain regarding functional outcomes and complications such as nonunion and malunion. Objective This study's objective is to evaluate the long-term functional outcomes and complications associated with non-surgical management of middle-third clavicular fractures. Methodology This prospective observational study was conducted at Mardan Medical Complex over 24 months. A total of 110 patients with isolated, closed, middle-third clavicle fractures treated conservatively were enrolled. Functional outcomes were assessed using the QuickDisabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand (QuickDASH) score and Constant-Murley Shoulder Score (CMSS) at 12-month follow-up. Radiological union, complications, and patient satisfaction were also recorded. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 25.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY). Independent t-tests and chi-square tests were applied where appropriate, with a p-value of < 0.05 considered statistically significant. Results Out of 110 enrolled patients, 102 (92.7%) completed follow-up. Union was achieved in 88 (86.3%) patients within 16 weeks. Nonunion occurred in seven (6.9%), and malunion in 10 (9.8%). The mean DASH score was 9.6 ± 7.2, and CMSS was 88.2 ± 6.8. Patients with union had significantly better scores (p < 0.001). Cosmetic dissatisfaction was reported in 18 (17.6%) patients, mostly associated with malunion. Conclusion Conservative management of midshaft clavicle fractures is generally effective, but functional outcomes are significantly influenced by healing quality. Careful patient selection and follow-up are essential to minimize complications and improve outcomes.
Keywords: clavicle fractures; conservative treatment; disabilities of the arm; fracture; fracture healing; malunited fractures; nonunion; shoulder and hand score; treatment outcome.
Copyright © 2025, Ahmad et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Informed consent for treatment and open access publication was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Medical Teaching Institution, Bacha Khan Medical College, Mardan issued approval 782/ORT/BKMC. Animal subjects: All authors have confirmed that this study did not involve animal subjects or tissue. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures



References
-
- Less than 1.5cm shortening in clavicle midshaft fracture has long-term functional impact. Pradel S, Brunaud M, Coulomb R, Kouyoumdjian P, Marès O. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2023;109:90. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
