Development of robust machine learning models to estimate hydrochar higher heating value and yield based upon biomass proximate analysis
- PMID: 41335148
- PMCID: PMC12675903
- DOI: 10.1186/s40643-025-00979-1
Development of robust machine learning models to estimate hydrochar higher heating value and yield based upon biomass proximate analysis
Abstract
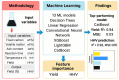
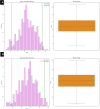
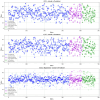
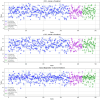
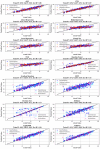
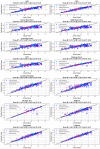
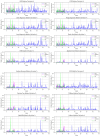
This study introduces a robust machine learning framework for predicting hydrochar yield and higher heating value (HHV) using biomass proximate analysis. A curated dataset of 481 samples was assembled, featuring input variables such as fixed carbon, volatile matter, ash content, reaction time, temperature, and water content. Hydrochar yield and HHV served as the target outputs. To enhance data quality, Monte Carlo Outlier Detection (MCOD) was employed to eliminate anomalous entries. Thirteen machine learning algorithms, including convolutional neural networks (CNN), linear regression, decision trees, and advanced ensemble methods (CatBoost, LightGBM, XGBoost) were systematically compared. CatBoost demonstrated superior performance, achieving an R2 of 0.98 and mean squared error (MSE) of 0.05 for HHV prediction, and an R2 of 0.94 with MSE of 0.03 for yield estimation. SHAP analysis identified ash content as the most influential feature for HHV prediction, while temperature, water content, and fixed carbon were key drivers of yield. These results validate the effectiveness of gradient boosting models, particularly CatBoost, in accurately modeling hydrothermal carbonization outcomes and supporting data-driven biomass valorization strategies.
Keywords: Biomass proximate analysis; CatBoost algorithm; Higher heating value (HHV); Hydrochar yield prediction; Machine learning.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Consent for publication: All authors agree to publish this work. Competing interests: None.
Figures











References
-
- Abbasi P, Aghdam SK-y, Madani M (2023) Modeling subcritical multi-phase flow through surface chokes with new production parameters. Flow Meas Instrum 89:102293
-
- Aghdam SK-y et al (2022) Thermodynamic modeling of saponin adsorption behavior on sandstone rocks: an experimental study. Arab J Sci Eng. 10.1007/s13369-022-07552-4
-
- Aghdam SK-y et al (2023) Thermodynamic modeling of saponin adsorption behavior on sandstone rocks: an experimental study. Arab J Sci Eng 48(7):9461–9476
-
- Ahmadi MA et al (2013) Evolving artificial neural network and imperialist competitive algorithm for prediction oil flow rate of the reservoir. Appl Soft Comput 13(2):1085–1098
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

