The genome sequence of the Panther Danio, Danio aesculapii Kullander & Fang, 2009
- PMID: 41341111
- PMCID: PMC12669980
- DOI: 10.12688/wellcomeopenres.25028.1
The genome sequence of the Panther Danio, Danio aesculapii Kullander & Fang, 2009
Abstract
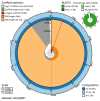
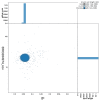
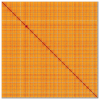
We present a genome assembly from a female specimen of Danio aesculapii (the Panther Danio; Chordata; Actinopteri; Cypriniformes; Cyprinidae). The genome sequence is 1,381.5 megabases in span. Most of the assembly is scaffolded into 25 chromosomal pseudomolecules. Gene annotation of this assembly on Ensembl identified 23,884 protein coding genes.
Keywords: Cypriniformes; Danio aesculapii; Panther Danio; chromosomal; genome sequence.
Copyright: © 2025 Howe K et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

