Molecular docking insights into miR-155 and VEGF synergy: colorectal cancer detection through AI-enhanced integration of molecular biomarkers and clinical risk assessment
- PMID: 41345725
- PMCID: PMC12683792
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-025-03348-y
Molecular docking insights into miR-155 and VEGF synergy: colorectal cancer detection through AI-enhanced integration of molecular biomarkers and clinical risk assessment
Abstract
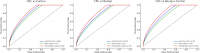
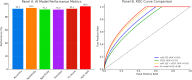
Colorectal cancer (CRC) remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, underscoring the need for non-invasive biomarkers that can support earlier detection and risk stratification. This exploratory study investigated the combined diagnostic performance of circulating microRNA-155 (miR-155) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in CRC, with mechanistic support from molecular docking and integration into an AI-based predictive model. In a case-control design, plasma levels of miR-155 and VEGF were quantified in CRC patients, individuals with benign colorectal conditions, and healthy controls. Diagnostic accuracy was assessed using ROC curve analysis, with comparisons across subgroup analyses (CRC vs benign, CRC vs controls, CRC vs benign + controls). Molecular docking provided comparative predictions of miR-155 interactions with regulatory proteins (IL-13RA1, SOCS1, PTEN, BCL-6, TP53INP1). An AI model (logistic regression with L2 regularization, stratified tenfold cross-validation) integrated biomarkers with clinical factors to evaluate predictive performance. Both miR-155 and VEGF were significantly elevated in CRC patients compared with benign and control groups. Individually, miR-155 achieved an AUC of 0.85 and VEGF an AUC of 0.79; combined analysis improved performance (AUC = 0.93). Subgroup ROC analyses confirmed robust discriminatory power across clinically relevant comparisons. The AI-integrated model achieved the highest accuracy (AUC = 0.96) under cross-validation. Docking suggested preferential interactions of miR-155 with IL-13RA1, SOCS1, and PTEN, supporting their mechanistic involvement. miR-155 and VEGF show promise as synergistic biomarkers for CRC detection, particularly when integrated with clinical risk factors. Molecular docking provides hypothesis-generating mechanistic insights, while AI modeling demonstrates the potential of multi-parametric integration. Given the modest, single-center sample size and lack of external validation, these findings should be considered exploratory. Larger, multi-center validation studies are essential before clinical translation.
Keywords: Biomarkers; CA19-9; CEA; Colorectal cancer; Diagnostic performance; ELISA; Early detection; MiR-155; QRT-PCR; VEGF.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: All participants provided written informed consent, and the study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Egyptian Liver Research Institute and Hospital (Approval# CTU2023-007). The research was conducted ethically following the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Competing interest: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Mohammed MA, Soffar AA, Yousef AI, Salama M, Ibrahim FAR, El-Sewedy T, et al. Usp6nl knockdown suppresses colorectal cancer progression by inducing CASP9-mediated apoptosis and disrupting FOXC2/SNAI1-driven EMT and angiogenesis. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025;25:153. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:233–54. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73:17–48. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

