The role of cyano-phycocyanin as a quorum sensing inhibitor to attenuate Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence
- PMID: 41346364
- PMCID: PMC12672448
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1624927
The role of cyano-phycocyanin as a quorum sensing inhibitor to attenuate Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence
Abstract
Introduction: In recent years, developing drugs that directly target pathways related to the pathogenic mechanisms of bacteria has been a research hotspot, and quorum sensing (QS) is one of the most effective strategies to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. We evaluated the inhibitory effect of cyano-phycocyanin (C-PC) on the virulence of PA2 in vitro and in vivo and explored its potential as a quorum sensing inhibitor (QSI).
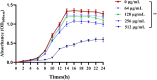
Methods: In this study, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and growth curve of C-PC on PA2 were determined, and the effect of C-PC on QS-regulated virulence factors and the anti-biofilm activity of C-PC against PA2 were investigated. The Pseudomonas quinolone signal (PQS) were analyzed by HPLC system and the expression levels of QS signaling molecules, virulence genes, biofilm and movement-related genes were detected by qPCR. The macrophage and mouse infection model were used to explore the anti-infection ability of C-PC in vitro and in vivo.
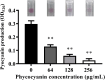
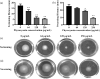
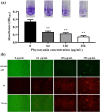
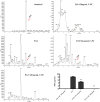
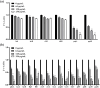
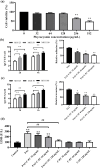
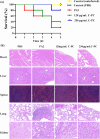
Results: C-PC attenuated biofilm formation, pyocyanin synthesis, motility, and PQS signaling molecule production. Moreover, C-PC significantly downregulated the transcription levels of QS-related genes in PA2, including pqsA and pqsR, as well as the expression of virulence factor genes phzA, lasA, lasB, flgF, fliE, exoS, exsA, lecA, popB, vasG, chiC, pelF, pslB, qseB, and pgsR. In vitro, C-PC reduced the adhesion and invasion of PA2 in RAW264.7 cells, and decreased LDH release and macrophage damage caused by PA2 infection. In vivo, C-PC reduced the pathogenicity of PA2 and improved mouse survival rates, showing a protective effect.
Conclusion: Taken together, these results suggest that C-PC showed strong anti-QS activity, providing new insights into the development of strategies against PA infection.
Keywords: C-PC; PQS; Pseudomonas aeruginosa; RAW264.7; biofilm.
Copyright © 2025 Ying, Guo, Pan, Li, Tai, Li, Lin, Pan, Huang, Xiao, Pan, Xu, Xie, Lou and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abdalla M. Y., Hoke T., Seravalli J., Switzer B. L., Bavitz M., Fliege J. D., et al. (2017). Pseudomonas quinolone signal induces oxidative stress and inhibits heme oxygenase-1 expression in lung epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 85, e00176–e00117. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00176-17, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmad I., Rouf S. F., Sun L., Cimdins A., Shafeeq S., Le Guyon S., et al. (2016). BcsZ inhibits biofilm phenotypes and promotes virulence by blocking cellulose production in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium. Microb. Cell Fact. 15, 177. doi: 10.1186/s12934-016-0576-6, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

