Radiomics Reproducibility in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis Based on PROSTATEx
- PMID: 41355262
- PMCID: PMC12688314
- DOI: 10.5213/inj.2550294.147
Radiomics Reproducibility in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis Based on PROSTATEx
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to extract radiomics features from prostate magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), evaluate their reproducibility, and determine whether machine learning (ML) models built on reproducible features can noninvasively diagnose prostate cancer (PCa).
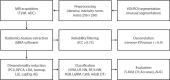
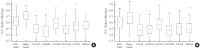
Methods: We analyzed prostate MRI from 82 subjects (41 PCa and 41 controls) in the public PROSTATEx dataset. From T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) maps, 215 features per sequence were extracted (T2WI 215; ADC 215; total 430). Reproducibility within each sequence was quantified after repeated segmentation using the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) with a 2-way random-effects, absolute-agreement model. Only shared features with ICC≥0.75 in both T2WI and ADC were retained. Selected features were normalized and combined via early fusion into a single input vector. Redundant features were eliminated by Pearson correlation analysis (|r|>0.9).
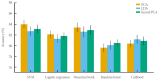
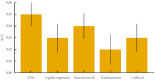
Results: Reproducible radiomics features (ICC≥0.75) were key contributors to model performance. Using these features, support vector machine, neural network, and logistic regression models achieved accuracies of 80%-84% and a maximum area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of 0.85 under 5-fold cross-validation. Principal component analysis yielded the most consistent results, whereas several nonlinear dimensionality reduction methods produced variable outcomes across classifiers.
Conclusion: Combining reproducible MRI radiomics features with dimensionality reduction and ML offers a robust noninvasive approach for PCa diagnosis. Emphasizing reproducibility enhances model performance and reliability, supporting potential clinical translation.
Keywords: Machine learning; Magnetic resonance imaging; Prostatic neoplasms; Radiomics; Reproducibility of results.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

