Research on Deep Learning-Based Human-Robot Static/Dynamic Gesture-Driven Control Framework
- PMID: 41374578
- PMCID: PMC12693889
- DOI: 10.3390/s25237203
Research on Deep Learning-Based Human-Robot Static/Dynamic Gesture-Driven Control Framework
Abstract
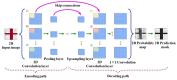
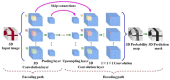
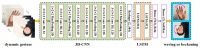
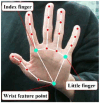
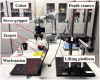
For human-robot gesture-driven control, this paper proposes a deep learning-based approach that employs both static and dynamic gestures to drive and control robots for object-grasping and delivery tasks. The method utilizes two-dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks (2D-CNNs) for static gesture recognition and a hybrid architecture combining three-dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks (3D-CNNs) and Long Short-Term Memory networks (3D-CNN+LSTM) for dynamic gesture recognition. Results on a custom gesture dataset demonstrate validation accuracies of 95.38% for static gestures and 93.18% for dynamic gestures, respectively. Then, in order to control and drive the robot to perform corresponding tasks, hand pose estimation was performed. The MediaPipe machine learning framework was first employed to extract hand feature points. These 2D feature points were then converted into 3D coordinates using a depth camera-based pose estimation method, followed by coordinate system transformation to obtain hand poses relative to the robot's base coordinate system. Finally, an experimental platform for human-robot gesture-driven interaction was established, deploying both gesture recognition models. Four participants were invited to perform 100 trials each of gesture-driven object-grasping and delivery tasks under three lighting conditions: natural light, low light, and strong light. Experimental results show that the average success rates for completing tasks via static and dynamic gestures are no less than 96.88% and 94.63%, respectively, with task completion times consistently within 20 s. These findings demonstrate that the proposed approach enables robust vision-based robotic control through natural hand gestures, showing great prospects for human-robot collaboration applications.
Keywords: deep learning; dynamic and static gesture; gesture-driven control framework; human-robot collaboration; three-dimensional Convolutional Neural Networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Zhang G., Xu Z., Hou Z., Yang W., Liang J., Yang G., Wang J., Wang H., Han C. A systematic error compensation strategy based on an optimized recurrent neural network for collaborative robot dynamics. Appl. Sci. 2020;10:6743. doi: 10.3390/app10196743. - DOI
-
- Patel H.K., Rai V., Singh H.R., Kumar R. Analyzing body language and facial expressions using machine learning techniques; Proceedings of the 2025 International Conference on Pervasive Computational Technologies (ICPCT); Greater Noida, India. 8–9 February 2025; pp. 629–633.
-
- Petrov M., Chibizov P., Sintsov M., Balashov M., Kapravchuk V., Briko A. Multichannel surface electromyography system for prosthesis control using RNN classifier; Proceedings of the 2023 Systems and Technologies of the Digital HealthCare (STDH); Tashkent, Uzbekistan. 4–6 October 2023; pp. 93–96.
-
- Scheck K., Ren Z., Dombeck T., Sonnert J., Gogh S.V., Hou Q., Wand M., Schultz T. Cross-speaker training and adaptation for electromyography-to-speech conversion; Proceedings of the 2024 46th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC); Orlando, FL, USA. 15–19 July 2024; pp. 1–4. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto Y. Lightweight and high accurate RR interval compensation for signals from wearable ECG sensors. IEEE Sens. Lett. 2024;8:1–4. doi: 10.1109/LSENS.2024.3398251. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 62073092/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- FJIES2024KF08/Open Fund of Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Special Intelligent Equipment Safety and Measurement & Control
- KF-01-22005/Open Fund of Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Intelligent Machining Technology and Equip-ment
- 2025J01985/Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province, China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

