New Benzimidazole-Based pH-Sensitive Fluorescent Probes
- PMID: 41375217
- PMCID: PMC12692881
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules30234622
New Benzimidazole-Based pH-Sensitive Fluorescent Probes
Abstract
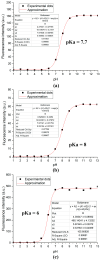
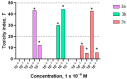
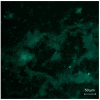
This article is devoted to the synthesis and investigation of a family of new benzimidazole compounds with a propylsulfonate moiety, synthesized by condensation of salicylic aldehyde or its 5-substituted derivatives with 3-(2,3-dimethylbenzimidazol-1-ium-1-yl)propane-1-sulfonate. The structure of the obtained dyes was confirmed using NMR, FT-IR, and HRMS. Absorption and photoluminescence properties were studied in phosphate buffers over a wide pH range, and changes in the absorption and fluorescence spectra of DMSO solutions upon titration with DIPEA and HCl were also studied. It was found that all the target compounds possess pH-sensitive optical properties and can be used as fluorescent probes, while methoxycarbonyl-substituted derivative 3c demonstrated the most prominent optical and fluorescent response starting from pH ~ 4.5. The toxicity of the compounds was studied using whole-cell bioluminescent bacterial sensors. The effect on the biomass and metabolic activity of strains Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538-P FDA 209-P and Escherichia CDC F-50 bacterial biofilms was also investigated. In the final stage of the study, bioimaging experiments were carried out using the selected most promising dye 3c and biofilms. It was demonstrated that the dye can be excited by light with wavelengths of 458 nm or 750 nm in multiphoton mode. Importantly, when biofilms are incubated in the dye solution for 3 h, only the extracellular matrix is stained. However, if the staining time is increased to 24 h, dye penetration into bacterial cells is observed, resulting in a second photoluminescence maximum during sample analysis. It is important to note that when biofilms are incubated in a dye solution for 3 h, only the extracellular matrix is stained, while with longer staining, penetration of the dye into bacterial cells is observed, and a second photoluminescence maximum appears during sample analysis. The results obtained demonstrate a high potential of using benzimidazole-based compounds as pH-sensitive fluorescent probes operating in a biologically relevant pH range, which can be used for imaging of bacterial biofilms.
Keywords: benzimidazole; bioimaging; fluorescence; molecular docking; pH; sulfonic acids; whole-cell lux-biosensors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Gottlieb R.A., Giesing H.A., Zhu J.Y., Engler R.L., Babior B.M. Cell acidification in apoptosis: Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor delays programmed cell death in neutrophils by up-regulating the vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1995;92:5965–5968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.13.5965. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

