Preparation and Application of Magnetic Microporous Organic Networks for Rapid Adsorption Enrichment of Multiple Mycotoxins in Complex Food Matrices
- PMID: 41375922
- PMCID: PMC12692691
- DOI: 10.3390/foods14233984
Preparation and Application of Magnetic Microporous Organic Networks for Rapid Adsorption Enrichment of Multiple Mycotoxins in Complex Food Matrices
Abstract
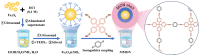
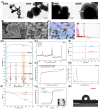
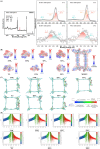
Mycotoxins commonly contaminate grains and traditional Chinese medicinal materials, posing serious health risks to humans and animals. To address this issue, a magnetic microporous organic network (MMON) was synthesized via an in situ growth method and Sonogashira-Hagihara coupling for the simultaneous adsorption of seven mycotoxins, followed by UPLC-MS/MS detection. The optimized MMON featured a high surface area, uniform micropores, and rapid magnetic separation within 5 s. Structural and compositional analyses confirmed its tailored architecture, while DFT calculations revealed a pore confinement effect, π-π stacking, and hydrophobic interactions as the primary adsorption mechanisms. A magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) method using 8 mg of MMON achieved adsorption equilibrium within 10 s in 5 mL of a 4 mg/L mycotoxin standard solution. The material maintained over 95% efficiency across ten reuse cycles at a low cost. Under optimal conditions, an MSPE-UPLC-MS/MS method with a low detection limit (0.002-0.15 μg/L), wide linear range (0.01-100.0 μg/L), large enrichment factor (20.1-21.9), low adsorbent dosage, and short extraction time was developed. The determination of mycotoxins in complex grain-based foods and herbal products was also realized with recoveries of 81.32% to 116.10%. This work offers a rapid, cost-effective, and high-throughput approach for mycotoxin detection, supporting quality control in food and herbal product safety.
Keywords: adsorption mechanism; complex matrix; magnetic microporous organic network; magnetic solid-phase extraction; mycotoxins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

