Changes in blood coagulation
- PMID: 5322193
- PMCID: PMC3035840
- DOI: 10.1001/archsurg.1966.01320190073016
Changes in blood coagulation
Figures
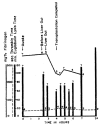





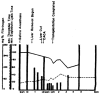
References
-
- von Kaulla KN, Schultz RL. Methods for Evaluation of Human Fibrinolysis: Studies With Two Combined Techniques. Amer J Clin Path. 1958;29:104. - PubMed
-
- Rahn B, von Kaulla KN. Pharmacological Induction of Fibrinolytic Activity in the Dog. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964;115:359. - PubMed
-
- Alkjaersig N, Fletcher AP, Sherry S. E-Aminocaproic Acid, an Inhibitor of Plasminogen Activation. J Biol Chem. 1959;234:832. - PubMed
-
- von Kaulla KN. Continuous Automatic Recording of Fibrin Formation and Fibrinolysis. J Lab Clin Med. 1957;49:304. - PubMed
-
- Ratnoff OD, Menzie C. New Method for Determination of Fibrinogen in Small Samples of Plasma. J Lab Clin Med. 1951;37:316. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

