Metabolism of normetanephrine-H3 in rat brain--identification of conjugated 3-methoxy-4-hydrophenylglycol as the major metabolite
- PMID: 5647052
- PMCID: PMC3051363
- DOI: 10.1016/0006-2952(68)90330-4
Metabolism of normetanephrine-H3 in rat brain--identification of conjugated 3-methoxy-4-hydrophenylglycol as the major metabolite
Abstract
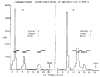
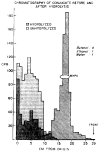
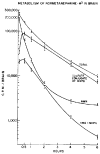
Normetanephrine-H3 injected into the cisterna magna of rats is rapidly metabolized and disappears from brain with an initial half-life of about 12 min. Monoamine oxidase inhibition prevents almost completely the conversion of normetanephrine-H3 to other metabolites and markedly diminishes the rate of disappearance of radioactivity from brain ( ). These data show that normetanephrine is normally metabolized primarily by monoamine oxidase and that unaltered normetanephrine does not readily pass out of the brain. Free 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylglycol (MHPG) and 3-methoxy-4-hydroxymandelic acid (VMA) formed from intracistemally injected normetanephrine-H3 represent only a small fraction of the radioactivity in brain. The major metabolite was identified as the sulfate conjugate of MHPG. After intracisternal administration of norepinephrine-H3, 3-methoxy-4-hydroxyphenylgIycol sulfate (MHPG-SO4) was also found to be the major metabolite present in brain. These findings suggest that deamination, reduction, and subsequent corrugation with sulfate is the primary route of metabolism of normetanephrine in rat brain and that norepinephrine is also metabolized to this sulfate conjugate.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

