Resolution of synthetic att-site Holliday structures by the integrase protein of bacteriophage lambda
- PMID: 6092961
- PMCID: PMC1965284
- DOI: 10.1038/311721a0
Resolution of synthetic att-site Holliday structures by the integrase protein of bacteriophage lambda
Abstract
Site-specific recombination of the bacteriophage lambda genome into and out of the host bacterial genome is postulated to involve the formation of Holliday structure intermediates by reciprocal single-strand exchanges. Synthetic analogues of the predicted recombination intermediates are resolved in vitro by the protein product of the lambda int gene. Some of the structural features and reaction conditions for this genetic recombination can now be defined.
Figures

 ) and bottom (
) and bottom (
 ) strands and the attB top (
) strands and the attB top (
 ) and bottom (
) and bottom (
 ) strands have their 5′ termini indicated by a knob. The cutting and exchange of two bottom strands (left) results in form ExI, whereas the cutting and exchange of two top strands (right) results in form ExII. In the case where attL and attR are the parental DNAs (not shown here), the cutting and exchange of the two top strands would result in form ExI and the cutting and exchange of the two bottom strands would result in form ExII.
) strands have their 5′ termini indicated by a knob. The cutting and exchange of two bottom strands (left) results in form ExI, whereas the cutting and exchange of two top strands (right) results in form ExII. In the case where attL and attR are the parental DNAs (not shown here), the cutting and exchange of the two top strands would result in form ExI and the cutting and exchange of the two bottom strands would result in form ExII.
 ) and bottom (
) and bottom (
 ) strands and the attB top (
) strands and the attB top (
 ) and bottom (
) and bottom (
 ) strands are also used to indicate the corresponding DNA strands in the prophage att sites BOP’ and POB’. The 5′ termini are marked with a knob. b, The ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel shows the four DNA restriction fragments before (lane 1) and after (lane 2) denaturation and after reannealing (lane 3). Electron micrograph shows DNA eluted from the gel band marked χ-form. Methods: 40-120 pmol of restriction fragments in 0.8-1.0 ml were denatured and reannealed by one of the following two procedures: (1), the DNAs were denatured by boiling at 100 °C for 2 min in 1 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 0.1 mM EDTA, followed by rapid chilling in ice water. One-tenth volume of 20 × SSC (3 M NaCl, 0.3 M Na citrate) was added and the mixture was placed in a 65 °C water bath that was then allowed to equilibrate to room temperature overnight. (2), DNA restriction fragments in low melting agarose were heated at 68 °C until the agarose was melted and then placed at 37 °C. They were then denatured in 0.1 M NaOH for 5 min; after adding ½ vol of deionized formamide and neutralizing with acetic acid, they were incubated at 37 °C overnight. The χ-forms were purified by gel electrophoresis in 1% agarose at 1.8 V cm−1 in E* buffer (18 mM NaCl, 2mM EDTA, 40 mM Tris, 20mM sodium acetate, adjusted to pH 8.0 with acetic acid). DNA was electroeluted from the excised gel band and purified by elution from a BND cellulose column as described previously.
) strands are also used to indicate the corresponding DNA strands in the prophage att sites BOP’ and POB’. The 5′ termini are marked with a knob. b, The ethidium bromide-stained agarose gel shows the four DNA restriction fragments before (lane 1) and after (lane 2) denaturation and after reannealing (lane 3). Electron micrograph shows DNA eluted from the gel band marked χ-form. Methods: 40-120 pmol of restriction fragments in 0.8-1.0 ml were denatured and reannealed by one of the following two procedures: (1), the DNAs were denatured by boiling at 100 °C for 2 min in 1 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.9), 0.1 mM EDTA, followed by rapid chilling in ice water. One-tenth volume of 20 × SSC (3 M NaCl, 0.3 M Na citrate) was added and the mixture was placed in a 65 °C water bath that was then allowed to equilibrate to room temperature overnight. (2), DNA restriction fragments in low melting agarose were heated at 68 °C until the agarose was melted and then placed at 37 °C. They were then denatured in 0.1 M NaOH for 5 min; after adding ½ vol of deionized formamide and neutralizing with acetic acid, they were incubated at 37 °C overnight. The χ-forms were purified by gel electrophoresis in 1% agarose at 1.8 V cm−1 in E* buffer (18 mM NaCl, 2mM EDTA, 40 mM Tris, 20mM sodium acetate, adjusted to pH 8.0 with acetic acid). DNA was electroeluted from the excised gel band and purified by elution from a BND cellulose column as described previously.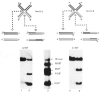

 ), which extends from 57.0% to 52.4% on the λ map and does not contain an att site, was cloned as a tandem duplication into the HindIII site of pBR322 (—), to generate plasmid pPH910. Three HinfI fragments of pPH910 were isolated for the χ-form construction: fragment II consists of the left pBR322-λ junction, fragment III of the head-to-tail junction of the two λ fragments, and fragment IV of the right λ-pBR322 junction. Fragment I is the pBR322 HinfI fragment into which the λ DNA had been inserted. For each fragment, and for each arm of the χ-structure, the amount (base pairs) of pBR322 DNA or λ DNA is indicated. Methods: The χ-form was generated by alkali denaturation and renaturation according to scheme (2) and purified by agarose gel electrophoresis as described in Fig. 2 legend.
), which extends from 57.0% to 52.4% on the λ map and does not contain an att site, was cloned as a tandem duplication into the HindIII site of pBR322 (—), to generate plasmid pPH910. Three HinfI fragments of pPH910 were isolated for the χ-form construction: fragment II consists of the left pBR322-λ junction, fragment III of the head-to-tail junction of the two λ fragments, and fragment IV of the right λ-pBR322 junction. Fragment I is the pBR322 HinfI fragment into which the λ DNA had been inserted. For each fragment, and for each arm of the χ-structure, the amount (base pairs) of pBR322 DNA or λ DNA is indicated. Methods: The χ-form was generated by alkali denaturation and renaturation according to scheme (2) and purified by agarose gel electrophoresis as described in Fig. 2 legend.
 ); the consensus recognition sequences (
); the consensus recognition sequences (
 ) and the approximate region of DNA covered (as determined by nuclease protection) for each of the following: the junction-type Int binding sites, C and C’ (
) and the approximate region of DNA covered (as determined by nuclease protection) for each of the following: the junction-type Int binding sites, C and C’ (
 ), the arm-type Int binding sites P1, P2, P’1, P’2, and P’3 (
), the arm-type Int binding sites P1, P2, P’1, P’2, and P’3 (
 ),, the IHF binding sites H1, H2 and H’ (
),, the IHF binding sites H1, H2 and H’ (
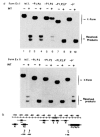
 ). The endpoints of att DNA in the three deletions used to construct the different χ-structures are indicated (−109, −89 and +46) (see Table 1). Each χ-form was incubated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of purified Int protein in a 20-μl reaction that contained ~0.01 μg of χ-forrn, 0.5 μg of supercoiled pBR322 DNA and 1 U of purified Int. After electrophoresis of the reaction products, gels were stained with ethidium bromide (0.5 μg ml−1) to visualize the nicking-closing activity of Int on the supercoiled pBR322 DNA. The expected levels of activity were observed in each case (data not shown). The 32P-labelled χ-forms and resolution products were visualized by autoradiography. The size (in base pairs) of each labelled resolution product is as follows: BB’, 940; BP’, 1,077; BΔ’, 886; PB’, 1,114; ΔB’, 972 (lane 4) and 952 (lanes 6 and 8). In this exposure of the autoradiogram, resolution products of similar size are not clearly resolved in several of the lanes; shorter exposures (and other gels) show that both resolution products are obtained in each reaction. The incomplete resolution observed in lane 6 of the upper gel is not typical; in other experiments in these conditions resolution is complete. Methods: Reaction conditions, processing and gel electrophoresis were as for Fig. 3, with no spermidine. For 32P labelling of forms ExI and ExII, the BOB’ HincII fragment was first labelled at the 5′ termini with polynucleotide kinase and then strand-separated by gel electrophoresis. The top strand of BOB’ was incorporated into form ExI and the bottom strand into form ExII (see Fig. 2) by annealing with the other three restriction fragments (Table 1). The specific activity is the same for the entire form ExI family (or the entire form ExII family), because the 32P label is always on the BOB’ strand which is common to all five χ-forms (see Table 1).
). The endpoints of att DNA in the three deletions used to construct the different χ-structures are indicated (−109, −89 and +46) (see Table 1). Each χ-form was incubated in the absence (−) or presence (+) of purified Int protein in a 20-μl reaction that contained ~0.01 μg of χ-forrn, 0.5 μg of supercoiled pBR322 DNA and 1 U of purified Int. After electrophoresis of the reaction products, gels were stained with ethidium bromide (0.5 μg ml−1) to visualize the nicking-closing activity of Int on the supercoiled pBR322 DNA. The expected levels of activity were observed in each case (data not shown). The 32P-labelled χ-forms and resolution products were visualized by autoradiography. The size (in base pairs) of each labelled resolution product is as follows: BB’, 940; BP’, 1,077; BΔ’, 886; PB’, 1,114; ΔB’, 972 (lane 4) and 952 (lanes 6 and 8). In this exposure of the autoradiogram, resolution products of similar size are not clearly resolved in several of the lanes; shorter exposures (and other gels) show that both resolution products are obtained in each reaction. The incomplete resolution observed in lane 6 of the upper gel is not typical; in other experiments in these conditions resolution is complete. Methods: Reaction conditions, processing and gel electrophoresis were as for Fig. 3, with no spermidine. For 32P labelling of forms ExI and ExII, the BOB’ HincII fragment was first labelled at the 5′ termini with polynucleotide kinase and then strand-separated by gel electrophoresis. The top strand of BOB’ was incorporated into form ExI and the bottom strand into form ExII (see Fig. 2) by annealing with the other three restriction fragments (Table 1). The specific activity is the same for the entire form ExI family (or the entire form ExII family), because the 32P label is always on the BOB’ strand which is common to all five χ-forms (see Table 1).References
-
- Nash HAA. Rev Genet. 1981;15:143–167. - PubMed
-
- Weisberg R, Landy A. In: Lambda II. Hendrix RW, Roberts JW, Stahl FW, Weisberg RW, editors. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; New York: 1983. pp. 211–250.
-
- Nash HA, Robertson CA. J biol Chem. 1981;256:9246–9253. - PubMed
-
- Abremski K, Gottesman S. J biol Chem. 1982;257:9658–9710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

