Maintenance of wakefulness test: a polysomnographic technique for evaluation treatment efficacy in patients with excessive somnolence
- PMID: 6177511
- PMCID: PMC2480525
- DOI: 10.1016/0013-4694(82)90142-0
Maintenance of wakefulness test: a polysomnographic technique for evaluation treatment efficacy in patients with excessive somnolence
Abstract
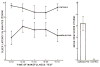
Ten patients with narcolepsy were given five 20 min opportunities to remain awake throughout the day. Trials were offered at 2 h intervals beginning at 10:00. Polysomnographic variables were monitored during each trial. Sleep latency increased when patients were instructed to maintain wakefulness compared to when instructed to sleep; however, sleep latencies were still lower for narcoleptics than for control subjects. Unexpectedly, we were not always able to document patients' reports of increased ability to stay awake. The findings suggested that clinical data on symptom control in narcolepsy do not predict ability to stay awake. Objective measures of the ability are potentially more useful in evaluating treatment.
Figures
References
-
- Association of Sleep Disorders Centers (H. Roffwarg) Diagnostic classification of sleep and arousal disorders. Sleep Disorders Classification Committee. Sleep. 1979;2:1–137. - PubMed
-
- Carskadon M, Dement W. Sleep studies on a 90-minute day. Electroenceph clin Neurophysiol. 1975;39:145–155. - PubMed
-
- Carskadon M, Dement W. Effects of total sleep loss on sleep tendency. Percept Mot Skills. 1979;48:495–506. - PubMed
-
- Hartse K, Roth T, Zorick F, Moyles T. REM sleep episodes during multiple daytime naps of narcoleptic subjects. Sleep Res. 1980a;9:203.
-
- Hartse K, Roth T, Zorick F, Zammit G. The effect of instruction upon sleep latency during multiple daytime naps of normal subjects. Sleep Res. 1980b;9:123.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical