The lambda phage att site: functional limits and interaction with Int protein
- PMID: 6246439
- PMCID: PMC1994824
- DOI: 10.1038/285085a0
The lambda phage att site: functional limits and interaction with Int protein
Abstract
Site specific integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda involves unequal partners. The minimal phage att site is composed of approximately 240-base pairs and four distinct binding sites for Int protein, at least three of which are crucial for function. This 'donor site' recombines efficiently with a smaller 'recipient site' that lacks the extensive interactions with Int protein.
Figures



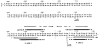
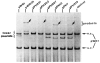
 ). Ambiguities in the precise boundaries of the protected regions are due to the failure of neocarzinostatin (●) or DNase I (○) to cut certain bases in the control digests. An inverted repeat structure (→ ←) which includes sequence from each of the two Int-binding sites plus additional sequence between the two sites is indicated.
). Ambiguities in the precise boundaries of the protected regions are due to the failure of neocarzinostatin (●) or DNase I (○) to cut certain bases in the control digests. An inverted repeat structure (→ ←) which includes sequence from each of the two Int-binding sites plus additional sequence between the two sites is indicated.

References
-
- Gottesman ME, Weisberg RA. In: The Bacteriophage Lambda. Hershey AD, editor. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; New York: 1971. pp. 113–138.
-
- Nash HA. Curr Topics Microbiol Immun. 1978;78:171–199. - PubMed
-
- Miller HI, Kikuchi A, Nash HA, Weisberg RA, Friedman DI. Cold Spring Harb Symp quant Biol. 1979;43:1121–1126. - PubMed
-
- Gottesman S, Abremski K. J molec Biol. 138 (in the press)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

