Sensitivity functions in the estimation of parameters of cellular exchange
- PMID: 6692937
- PMCID: PMC4132824
Sensitivity functions in the estimation of parameters of cellular exchange
Abstract
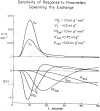
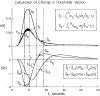
The analysis of multiple-indicator dilution curves to estimate the rates of transport of ions and substrates across the sarcolemma of myocardial cells requires the formulation of models for the blood-interstitial fluid-cell exchanges. The fitting of models to the sets of experimental data is dependent on acquiring a large enough data set, in one physiological state, that there is at least as much information in the data as there are unknown model parameters to be determined. Inasmuch as data are necessarily noisy, redundancy of data and overdetermination of the unknowns are highly desirable. Sensitivity functions are useful in demonstrating which portions of the data relate to which unknown parameters. They are also useful in adjusting model parameters to fit the model to the data, and therefore in parameter evaluation.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
