Does weight loss cause the exercise-induced increase in plasma high density lipoproteins?
- PMID: 6870998
- PMCID: PMC2821585
- DOI: 10.1016/0021-9150(83)90153-3
Does weight loss cause the exercise-induced increase in plasma high density lipoproteins?
Abstract
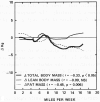
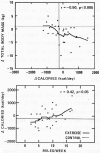
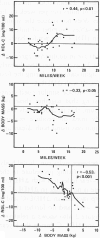
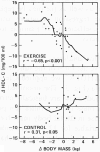
Studies showing an increase in plasma concentration of high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) with moderate exercise have usually rejected the role of body weight change in the HDL-C raising process, ostensibly because the amount of weight lost has been negligible. To investigate HDL-C changes more thoroughly, we followed initially sedentary middle-aged men randomly assigned to either a moderate running (n = 36) or a sedentary control (n = 28) group for one year. Among runners, one-year changes in plasma HDL-C concentrations correlated strongly with their body weight changes (r = - 0.53, P less than 0.001). Curve-fitting procedures and regression analysis suggested that processes associated with weight change produce much of the plasma HDL-C changes induced by moderate exercise and that changes in HDL-C concentration predominantly reflect changes in the reputedly anti-atherogenic HDL2 sub-component. Further, the interaction between weight change and plasma HDL-C concentration was significantly different (P less than 0.001) in exercisers and controls suggesting that the metabolic consequences of exercise-induced weight change are different from the consequences of weight change in the sedentary state.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effects of running mileage and duration on plasma lipoprotein levels.JAMA. 1982 May 21;247(19):2674-9. JAMA. 1982. PMID: 6952022 Clinical Trial.
-
Increased exercise level and plasma lipoprotein concentrations: a one-year, randomized, controlled study in sedentary, middle-aged men.Metabolism. 1983 Jan;32(1):31-9. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(83)90152-x. Metabolism. 1983. PMID: 6848894 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of weight loss by exercise or by dieting on plasma high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels in men with low, intermediate, and normal-to-high HDL at baseline.Metabolism. 1994 Jul;43(7):917-24. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(94)90277-1. Metabolism. 1994. PMID: 8028519 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
High density lipoprotein cholesterol and body composition of female runners.Metabolism. 1981 Oct;30(10):994-5. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(81)90099-8. Metabolism. 1981. PMID: 7278652
-
The influence of exercise on the concentrations of triglyceride and cholesterol in human plasma.Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1984;12:205-44. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 1984. PMID: 6376133 Review.
Cited by
-
Regression from prediabetes to normal glucose regulation is associated with reduction in cardiovascular risk: results from the Diabetes Prevention Program outcomes study.Diabetes Care. 2014 Sep;37(9):2622-31. doi: 10.2337/dc14-0656. Epub 2014 Jun 26. Diabetes Care. 2014. PMID: 24969574 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of aerobic exercise training on the lipid-lipoprotein profile of children and adolescents.Sports Med. 2000 Feb;29(2):99-112. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200029020-00003. Sports Med. 2000. PMID: 10701713 Review.
-
Correlates of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol in black and white women.Am J Public Health. 1994 Jan;84(1):98-101. doi: 10.2105/ajph.84.1.98. Am J Public Health. 1994. PMID: 8279620 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of weight-loss by exercise and by diet on apolipoproteins A-I and A-II and the particle-size distribution of high-density lipoproteins in men.Metabolism. 1992 Apr;41(4):441-9. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(92)90082-l. Metabolism. 1992. PMID: 1556953 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of low-fat diet, calorie restriction, and running on lipoprotein subfraction concentrations in moderately overweight men.Metabolism. 1994 May;43(5):655-63. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(94)90210-0. Metabolism. 1994. PMID: 8177056 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Wood PD, Haskell WL. Effects of exercise on plasma high-density lipoproteins. Lipids. 1979;14:415. - PubMed
-
- Adner MM, Castelli WP. Elevated high-density lipoprotein levels in marathon runners. J Amer Med Ass. 1980;243:534. - PubMed
-
- Keins B, Jorgensen I, Lewis S, et al. Increased plasma HDL-cholesterol and apo A-I in sedentary middle-aged men after physical conditioning. Europ J Clin Invest. 1980;10:203. - PubMed
-
- Huttunen JK, Lansimies E, Voutilainen E. Effects of moderate physical exercise on serum lipoproteins. Circulation. 1979;60:1220. - PubMed
-
- Kannel WB, Gordon T, Castelli WP. Obesity, lipids and glucose intolerance The Framingham Study. Amer J Ciin Nutr. 1979;32:1238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

