Correlation of early reduction in the apparent diffusion coefficient of water with blood flow reduction during middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats
- PMID: 7500876
- PMCID: PMC2733355
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.1910340314
Correlation of early reduction in the apparent diffusion coefficient of water with blood flow reduction during middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats
Abstract
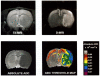
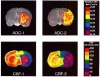
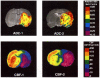
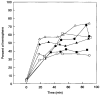
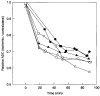
To determine the relationship between reductions in the apparent diffusion coefficient of water (ADC) and in cerebral blood flow (CBF) during focal ischemia, we used diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance (D-MR) imaging and autoradiographic CBF analysis to examine rats subjected to 30 or 90 min of permanent middle cerebral artery (MCA) occlusion. In the 30-min occlusion group (n = 10), the area with substantially reduced ADC (15% or more below the contralateral level [ADC15]) corresponded best to the area with CBF below 25 ml/100 g/min and was significantly smaller than the area with CBF below 50 ml/100 g/min (CBF50), a level associated with reduced protein synthesis and delayed necrosis (40 +/- 13% versus 74 +/- 8% of the ischemic hemisphere; P < 0.0001). In the 90-min occlusion group (n = 6), the ADC15 area corresponded best to the CBF30 to CBF35 area and was again significantly smaller than the CBF50 area (54 +/- 13% versus 73 +/- 20%, P < 0.05). Thus, the area of substantially reduced ADC at 30 and 90 min represents only 53% and 74%, respectively, of the tissue at risk for infarction. These findings indicate a potential limitation in using early D-MR imaging to predict stroke outcome.
Figures
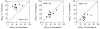

References
-
- Moseley ME, Cohen Y, Mintorovitch J, Chileuitt L, Shimizu H, Kucharczyk J, Wendland MF, Weinstein PR. Early detection of regional cerebral ischemia in cats: comparison of diffusion- and T2-weighted MRI and spectroscopy. Magn. Reson. Med. 1990;14:330–346. - PubMed
-
- Roussel SA, van Bruggen N, King MD, Houseman J, Williams SR, Gadian DG. Monitoring the initial expansion of focal ischaemic changes by diffusion-weighted MRI using a remote controlled method of occlusion. NMR Biomed. 1994;7:21–28. - PubMed
-
- Warach S, Chien D, Li W, Ronthal M, Edelman RR. Fast magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging of acute human stroke. Neurology. 1992;42:1717–1723. Published erratum appears in Neurology 1992 Nov; 42(11), 2192. - PubMed
-
- Zhong J, Petroff 0A, Prichard JW, Gore JC. Changes in water diffusion and relaxation properties of rat cerebrum during status epilepticus. Magn. Reson. Med. 1993;30:241–246. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

