Glutamatergic and cholinergic projections to the pontine inhibitory area identified with horseradish peroxidase retrograde transport and immunohistochemistry
- PMID: 7505295
- PMCID: PMC9046457
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.903360302
Glutamatergic and cholinergic projections to the pontine inhibitory area identified with horseradish peroxidase retrograde transport and immunohistochemistry
Abstract
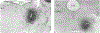
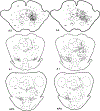
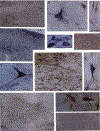
Previous studies in our laboratory have shown that microinjection of acetylcholine and non-N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate agonists into the pontine inhibitory area (PIA) induce muscle atonia. The present experiment was designed to identify the PIA afferents that could be responsible for these effects, by use of retrograde transport of wheat germ agglutinin conjugated horseradish peroxidase (WGA-HRP), glutamate immunohistochemistry and NADPH-diaphorase staining techniques. Experiments were performed in both decerebrate and intact cats. Dense retrograde WGA-HRP labelling was found in neurons in the periaqueductal gray (PAG) and mesencephalic reticular formation (MRF) at the red nucleus (RN) level, ventral portion of paralemniscal tegmental field (vFTP), retrorubral nucleus (RRN), contralateral side of PIA (cPIA), pontis reticularis centralis caudalis (PoC), and most rostral portion of the nucleus parvicellularis (NPV) and nucleus praepositus hypoglossi (PH) at the level of the pontomedullary junction; moderate labelling was seen in pedunculopontine nucleus, pars compacta (PPNc), laterodorsal tegmental nucleus (LDT), superior colliculus (SC), MRF and PAG at the level caudal to RN, medial and superior vestibular nuclei, and principle sensory trigeminal nucleus (5P); and light labelling was seen in dorsal raphe (DR) and locus coeruleus complex (LCC). The projection neurons were predominantly ipsilateral to the injection site, except for both vFTP and RRN, which had more projection cells on the contralateral side. Double labelled WGA-HRP/NADPH-d neurons could be found in PPNc and LDT. Double labelled WGA-HRP/glutamatergic neurons could be seen at high densities in MRF, RRN, vFTP, and cPIA, moderate densities in SC, LDT, PPNc, PoC, and NPV, and low densities in PH, 5P, DR, LCC, and PAG.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Figures

References
-
- Beitz AJ, Larson AA, Monaghan P, Altschuler RA, Mullet MM, and Madl JE (1986) Immunohistochemical localization of glutamate, glutaminase, and aspartate aminotransferase in neurons of the pontine nuclei of the rat. Neuroscience 17:741–753. - PubMed
-
- Berman AL (1968) The Brain Stem of the Cat Madison: University of Wisconsin Press.
-
- Fonnum F (1991) Neurochemical studies on glutamate-mediated neuro-transmission. In Meldrum BS, Moroni F, Simon RP, and Woods JH (eds): Excitatory Amino Acids New York: Raven Press, pp. 15–25.
-
- George R, Haslett WL, and Jenden DJ (1964) A cholinergic mechanism in the brainstem reticular formation: Induction of paradoxical sleep. Int. J. Neuropharmacol 3:541–552. - PubMed
-
- Hepler JR, Petrusz P, and Rustioni A (1986) Antisera to GABA, glutamate and aspartate: Characterization by immunoabsorption and immunocytochemistry. J. Histochem. Cytochem 34:110. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

