Translation-targeted therapeutics for viral diseases
- PMID: 7549467
- PMCID: PMC6134364
Translation-targeted therapeutics for viral diseases
Abstract
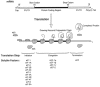
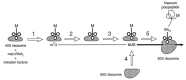
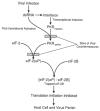
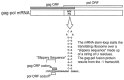
Viruses utilize the protein synthetic machinery of their host. Nonetheless, certain features of the synthesis of viral proteins are distinct from those of host-cell translation. Examples include internal ribosome entry sites in some viral mRNAs and ribosomal frameshifting during production of retroviral proteins. Viruses often inhibit host translation and/or possess mechanisms leading to preferential synthesis of viral proteins. In addition, a participant in the cellular antiviral response is the enzyme PKR (protein kinase, RNA activated), which is involved in the control of cellular translation. Thus, viruses and host cells wage war on the battlefield of translation. The distinctive features of protein synthesis in virally infected cells provide potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Translation-targeted therapeutics have precedence in antibiotics like tetracycline and erythromycin. Means for discovery of translation-targeted therapeutics for viral disease are discussed.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
