Human rheumatoid B-1a (CD5+ B) cells make somatically hypermutated high affinity IgM rheumatoid factors
- PMID: 7686945
- PMCID: PMC4625548
Human rheumatoid B-1a (CD5+ B) cells make somatically hypermutated high affinity IgM rheumatoid factors
Abstract
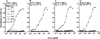
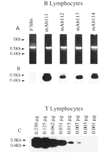
To analyze the structure and formally ascertain the B-1a cellular origin of IgM rheumatoid factor (RF) autoantibodies, we generated 4 IgM RF mAb-producing cell lines using sorted (surface CD5+) B-1a cells from a patient with active rheumatoid arthritis. The RF mAb111, mAb112, mAb113, and mAb114 were monoreactive and displayed a relatively high affinity for human IgG Fc fragment (Kd, 3.1 x 10(-7) to 6.8 x 10(-7) M). The B-1a origin of the lymphocytes that gave rise to the IgM RF was confirmed by the expression of surface CD5 and specific CD5 mRNA by all mAb-producing cell lines. Analysis of the genes encoding the RF mAb VH and VL regions revealed that members of the VHI and VHIII families were utilized in conjunction with V kappa IIIa, V kappa IIIb, or V lambda I genes. JH3 and JH4 genes were each utilized twice. The H chain CDR3 sequences were divergent and variable in length. The RF mAb VH genes were identical or closely related to those expressed in the "restricted" fetal B cell repertoire and/or were JH-proximal. For instance, mAb111 VH gene likely constituted a mutated variant of the expressed fetal 20P3 which is the second most JH-proximal gene (125 kb from JH). In addition, the expressed VH and VL genes were among those that have been found to encode other RF, different autoantibodies, high affinity antibodies induced by exogenous Ag, and natural autoantibodies in the adult and neonatal B cell repertoires. When compared with those of known germline genes, the expressed V gene sequences displayed a number of differences. By cloning and sequencing DNA from PMN of the same patient whose B lymphocytes were used for the mAb generation, we showed that such differences resulted from somatic hypermutation in the RF mAb112 VH gene. The germline gene (112GL) that presumably gave rise to the RF mAb112 VH segment was identical to the expressed fetal 51P1 gene. The distribution and the high replacement to silent mutation ratio of the nucleotide mutations in RF mAb112 VH segment were highly consistent with their selection by Ag. RF mAb113 was clonally related to RF mAb112, as shown by the utilization of the same sets of VHI-D-JH4 and V kappa IIIb-J kappa 4 genes, displaying identical junctional sequences, and the presence of two identical replacement and one silent mutations.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Figures





References
-
- Carson DA, Chen PP, Fox RI, Kipps TJ, Jirik F, Goldfien RD, Silverman G, Radoux V, Fong S. Rheumatoid factors and immune networks. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1987;5:109. - PubMed
-
- Chen PP, Silverman GP, Liu M-F, Carson DA. Idiotypic and molecular characterization of human rheumatoid factors. In: Carson DA, Chen PP, Kipps TJ, editors. Idiotypes in Biology and Medicine. Vol. 48. Basel: Chem. Immunol., S. Karger; 1990. p. 63. - PubMed
-
- Chen PP, Olsen NJ, Yang P-M, Soto-Gil RW, Olee T, Siminovitch KA, Carson DA. From human autoantibodies to fetal antibody repertoire to B cell malignancy: it’s a small world after all. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1990;5:239. - PubMed
-
- Avrameas S. Natural autoantibodies: from “horror autotoxicus” to “gnothi seauton.”. Immunol. Today. 1991;12:154. - PubMed
-
- Riboldi P, Kasaian MT, Mantovani L, Ikematsu H, Casali P. Natural antibodies. In: Bona CA, Siminovitch K, Zanetti M, Theofilopoulos AN, editors. The Molecular Pathology of Autoimmune Diseases. Philadelphia, PA: Gordon and Breach Science Publishers; 1993. pp. 45–64.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
