Mechanisms of baroreceptor activation
- PMID: 7735260
- PMCID: PMC12010917
- DOI: 10.3109/10641969509087050
Mechanisms of baroreceptor activation
Abstract
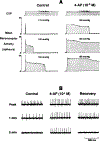
The determinants of the nerve activity generated at the baroreceptor endings have been examined. 1) In the isolated carotid sinus, the placement of activated bovine aortic endothelial cells decreased baroreceptor activity (BRA) in a reversible manner. Both endothelin and nitric oxide (NO) suppress BRA, whereas prostacyclin (PGI2) increases activity. 2) The BRA in single units declines and often ceases during non-pulsatile increases in carotid sinus pressure sustained over several minutes. This "adaptation" is attenuated by the transient potassium channel (IA) blocker 4-aminopyridine (4-AP) and not by inhibition of the Na+/K+ pump. 3) In preliminary studies, mechano-electrical transduction was examined in isolated and cultured nodose ganglion neurons. Opening of stretch-activated (SA) channels by suction on the cell-attached patch was seen infrequently; however, probing the neurons consistently increased their intracellular calcium [Ca++]i measured with fura-2. This increase in [Ca++]i is blocked by gadolinium (Gd3+), a trivalent lanthanide reported to block SA channels. Gd3+ also blocks the BRA in the carotid sinus. We conclude that paracrine factors significantly modulate BR sensitivity, that selective ionic mechanisms (the 4-AP sensitive K+ channels) determine the degree of "adaptation" of BR to elevated pressure, and that SA channels sensitive to Gd3+ may be the mechano-electrical transducers in BR neurons.
Figures
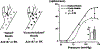
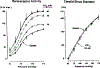
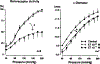

Similar articles
-
Modulation of baroreceptor activity by ionic and paracrine mechanisms: an overview.Braz J Med Biol Res. 1994 Apr;27(4):1001-15. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1994. PMID: 7522078 Review.
-
Mechanism of baroreceptor adaptation in dogs: attenuation of adaptation by the K+ channel blocker 4-aminopyridine.J Physiol. 1993 Mar;462:291-306. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019556. J Physiol. 1993. PMID: 8331585 Free PMC article.
-
Gadolinium inhibits mechanoelectrical transduction in rabbit carotid baroreceptors. Implication of stretch-activated channels.J Clin Invest. 1994 Dec;94(6):2392-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI117605. J Clin Invest. 1994. PMID: 7527431 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of effect of 4-aminopyridine on acute resetting of the type I carotid baroreceptor.Neurosci Lett. 1994 May 23;173(1-2):45-9. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(94)90146-5. Neurosci Lett. 1994. PMID: 7936421
-
Mechanisms of resetting of arterial baroreceptors: an overview.Am J Med Sci. 1988 Apr;295(4):327-34. doi: 10.1097/00000441-198804000-00019. Am J Med Sci. 1988. PMID: 2834951 Review.
Cited by
-
Translational neurocardiology: preclinical models and cardioneural integrative aspects.J Physiol. 2016 Jul 15;594(14):3877-909. doi: 10.1113/JP271869. Epub 2016 Jun 17. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27098459 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Arterial Baroreceptor Remodeling in Cardiovascular Diseases and Diabetes.Neurosci Bull. 2019 Feb;35(1):98-112. doi: 10.1007/s12264-018-0274-y. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Neurosci Bull. 2019. PMID: 30146675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vivo assessment of neurocardiovascular regulation in the mouse: principles, progress, and prospects.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011 Sep;301(3):H654-62. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00355.2011. Epub 2011 Jun 24. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21705676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The sympathetic nervous system in healthy and hypertensive pregnancies: physiology or pathology?Exp Physiol. 2023 Oct;108(10):1238-1244. doi: 10.1113/EP089665. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Exp Physiol. 2023. PMID: 36459575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baroreflex control of muscle sympathetic nerve activity: a nonpharmacological measure of baroreflex sensitivity.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010 Mar;298(3):H816-22. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00924.2009. Epub 2009 Dec 11. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20008270 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rubanyi GM, Romero JC, Vanhoutte PM: Flow-induced release of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Am. J. Physiol (1986) 250:H1145–H1149. - PubMed
-
- Karwatowska-Prokopczuk E, Ciabattoni G. Wennmalm, A.: Effects of hydrodynamic forces on coronary production of prostacyclin and purines. Am. J. Physiol (1989) 256 (Heart Circ. Physiol. 25):H:1532–H1538. - PubMed
-
- Brown AM: Receptors under pressure: an update on baroreceptors. Circ. Res (1980) 46:1–10. - PubMed
-
- Dorward PK, Andresen MC, Burke SL, Oliver JR, Korner PI: Rapid resetting of the aortic baroreceptors in the rabbit and its implications for short-term and longer term reflex control. Circ. Res (1982) 50:428–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
