Multi-shot EPI for improvement of myocardial tag contrast: comparison with segmented SPGR
- PMID: 7760715
- PMCID: PMC2396266
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.1910330321
Multi-shot EPI for improvement of myocardial tag contrast: comparison with segmented SPGR
Abstract
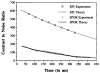
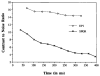
To assess the potential value of multi-shot EPI relative to segmented k-space SPGR for myocardial tagging, we measured tag contrast for both sequences in a phantom and human study and compared it with theoretical predictions. In the human heart, EPI tag contrast was three times that of SPGR at the end of systole. Tag duration was lengthened with EPI to at least 600 ms. In addition, the entire heart was examined in a total of 32 heartbeats with EPI versus 152 heartbeats with SPGR.
Figures



References
-
- Zerhouni EA, Parish DM, Rogers WJ, Yang A, Shapiro EP. Human heart: tagging with MR imaging-method for noninvasive assessment of myocardial motion. Radiology. 1988;169:59. - PubMed
-
- Axel L, Dougherty L. MR imaging of motion with spatial modulation of magnetization. Radiology. 1989;171:841–849. - PubMed
-
- Young AA, Axel L, Dougherty L, Bogen DK, Parenteau CS. Validation of tagging with MR imaging to estimate material deformation. Radiology. 1993;188(1):101–108. - PubMed
-
- Atkinson DJ, Edelman RR. Cineangiography of the heart in a single breath hold with a segmented turbo FLASH sequence. Radiology. 1991;178:357–360. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

