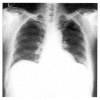
A case of noncardiogenic pulmonary edema by ethanolamine oleate
- PMID: 7865488
- PMCID: PMC4532062
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1994.9.2.125
A case of noncardiogenic pulmonary edema by ethanolamine oleate
Abstract
Endoscopic injection of sclerosing agents is a strategy for control of esophageal varix bleeding. Five percent solution of ethanolamine oleate(EO) has been used as sclerosing agent. It is well known that intravascular injection of oleic acid induces acute respiratory failure in animal models. However, EO-induced noncardiogenic pulmonary edema has not been reported in human. We report a case of noncardiogenic pulmonary edema developed after therapeutic trial of EO as sclerosing agent for esophageal varix.
Figures
References
-
- Hedberg SE, Fowler DL, Ryan RL. Injection sclerotherapy of esophageal varices using ethanolamine oleate. Am J Surg. 1981;143:426. - PubMed
-
- Iso Y, Kitano S, Iwanaga T, Hashizume M, Sugimachi K. Morphological and hemodynamic changes of the lung after injectio of 5% ethanolamine oleate into dogs. Eur Surg Res. 1989;21:175. - PubMed
-
- Suzuki N, Nakao A, Nonami T, Takagi H. Experimental study on the effects of sclerosants for esophageal varies on blood coagulation, fibrinolysis and systemic hemodynamics. Gastroenterol-Jpn. 1992;27:309. - PubMed
-
- Ashbaugh DG, Bigelow DB, Petty TL, Levine BE. Acute respiratory distress in adults. Lancet. 1967;2:319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources