DNA replication triggered by double-stranded breaks in E. coli: dependence on homologous recombination functions
- PMID: 7923355
- PMCID: PMC2988837
- DOI: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90279-8
DNA replication triggered by double-stranded breaks in E. coli: dependence on homologous recombination functions
Abstract
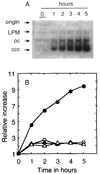
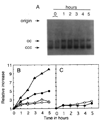
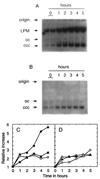
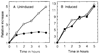
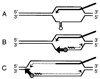
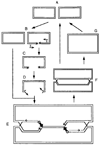
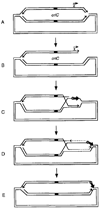
Homologous recombination-dependent DNA replication (RDR) of a lambda cos site-carrying plasmid is demonstrated in E. coli cells when the cells express lambda terminase that introduces a double-stranded break into the cos site. RDR occurs in normal wild-type cells if the plasmid also contains the recombination hotspot chi. Chi is dispensable when cells are induced for the SOS response or contain a recD mutation. recBC sbcA mutant cells are also capable of RDR induction. A recN mutation greatly reduces RDR in normal cells, but not in SOS-induced cells. RDR proceeds by the theta mode or rolling circle mode of DNA synthesis, yielding covalently closed circular plasmid monomers or linear plasmid multimers, respectively. Previously described inducible stable DNA replication is considered to be a special type of RDR that starts exclusively from specific sites (oriMs) on the chromosome.
Figures
References
-
- Asai T, Imai M, Kogoma T. DNA damage-inducible replication of the Escherichia coli chromosome is initiated at separable sites within the minimal oriC. J. Mol. Biol. 1994;235:1459–1469. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

