Selective ligands for rat A3 adenosine receptors: structure-activity relationships of 1,3-dialkylxanthine 7-riboside derivatives
- PMID: 7966162
- PMCID: PMC5875426
- DOI: 10.1021/jm00049a021
Selective ligands for rat A3 adenosine receptors: structure-activity relationships of 1,3-dialkylxanthine 7-riboside derivatives
Abstract
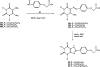
1,3-Dibutylxanthine 7-riboside has been found to be a partial agonist at A3 adenosine receptors (van Galen et al. Mol. Pharmacol. 1994, 45, 1101-1111). 1,3-Dialkylxanthine 7-riboside analogues modified at the 1-, 3-, and 8-purine positions and at the ribose 5'-position were synthesized. The nucleoside analogues were examined for affinity in radioligand binding assays at rat brain A3 adenosine receptors stably expressed in CHO cells, using the radioligand [[125I]-4-amino-3-iodobenzyl]adenosine-5'-N-methyluronamide (AB-MECA). Affinity was assayed at rat brain A1 and A2a receptors using [3H]PIA and [3H]CGS 21680, respectively. The affinity of xanthine 7-ribosides at A3 receptors depended on the 1,3-dialkyl substituents in the order: Pent > or = Bu >> Hx > Pr approximately Me. 1,3-Dipentylxanthine 7-riboside was slightly selective for A3 receptors (2-fold vs A1 and 10-fold vs A2a). 8-Methoxy substitution was tolerated at A3 receptors. 2-Thio vs 2-oxo substitution increased potency at all three subtypes and slightly increased A3 vs A1 selectivity. The 5'-uronamide modification, which was previously found to enhance A3 selectivity in N6-benzyladenosine derivatives, was also incorporated into the xanthine 7-ribosides, with similar results. The affinity of 1,3-dialkylxanthine 7-riboside 5'-uronamides at A3 receptors depended on the N-alkyluronamide substituent in the order: MeNH > EtNH >> NH2 >> Me2N. Affinity of the 5'-uronamides at A3 receptors was dependent on the 1,3-dialkyl substitution in the order: Bu > Pent > Hex. 1,3-Dibutylxanthine 7-riboside 5'-N-methylcarboxamide, with a Ki value of 229 nM at A3 receptors, was 160-fold selective for rat A3 vs A1 receptors and > 400-fold selective vs A2a receptors. This derivative acted as a full agonist in the A3 receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase.
Figures

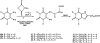

Similar articles
-
Structure-activity relationships of 1,3-dialkylxanthine derivatives at rat A3 adenosine receptors.J Med Chem. 1994 Sep 30;37(20):3373-82. doi: 10.1021/jm00046a022. J Med Chem. 1994. PMID: 7932565 Free PMC article.
-
Structure-activity relationships of 9-alkyladenine and ribose-modified adenosine derivatives at rat A3 adenosine receptors.J Med Chem. 1995 May 12;38(10):1720-35. doi: 10.1021/jm00010a017. J Med Chem. 1995. PMID: 7752196 Free PMC article.
-
2-Substitution of N6-benzyladenosine-5'-uronamides enhances selectivity for A3 adenosine receptors.J Med Chem. 1994 Oct 14;37(21):3614-21. doi: 10.1021/jm00047a018. J Med Chem. 1994. PMID: 7932588 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A3 receptors: novel ligands and paradoxical effects.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1998 May;19(5):184-91. doi: 10.1016/s0165-6147(98)01203-6. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1998. PMID: 9652191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Purine derivatives as ligands for A3 adenosine receptors.Curr Top Med Chem. 2005;5(13):1275-95. doi: 10.2174/156802605774463079. Curr Top Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 16305531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Activation of Phosphoinositide Breakdown and Elevation of Intracellular Calcium in a Rat RBL-2H3 Mast Cell Line by Adenosine Analogs: Involvement of A(3)-Adenosine Receptors?Drug Dev Res. 1996 Sep 1;39(1):36-46. doi: 10.1002/(sici)1098-2299(19960901)39:1<36::aid-ddr5>3.0.co;2-l. Drug Dev Res. 1996. PMID: 23087534 Free PMC article.
-
A3-adenosine receptors: design of selective ligands and therapeutic prospects.Drugs Future. 1995 Jul;20(7):689-699. doi: 10.1358/dof.1995.020.07.531583. Drugs Future. 1995. PMID: 25242859 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Medicinal chemistry of the A3 adenosine receptor: agonists, antagonists, and receptor engineering.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009;(193):123-59. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-89615-9_5. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19639281 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-Based Screening of Uncharted Chemical Space for Atypical Adenosine Receptor Agonists.ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Oct 21;11(10):2763-2772. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.6b00357. Epub 2016 Aug 22. ACS Chem Biol. 2016. PMID: 27439119 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and purine receptor affinity of 6-oxopurine nucleosides and nucleotides containing (N)-methanocarba-pseudoribose rings.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001 Sep 3;11(17):2295-300. doi: 10.1016/s0960-894x(01)00450-4. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2001. PMID: 11527718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maenhaut C, Sande Jv, Libert F, Abramowicz M, Parmentier M, Vanderhaegen JJ, Dumont JE, Vassart G, Schiffmann S. RDC8 codes for an adenosine A2 receptor with physiological constitutive activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990;173:1169–1178. - PubMed
-
- Stiles GL. Adenosine receptors. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:6451–6454. - PubMed
-
- Ali H, Cunha-Melo JR, Saul WF, Beavan MF. Activation of phospholipase C via adenosine receptors provides synergistic signals for secretion in antigen stimulated RBL-2H3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990;265:745–753. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
