Labeling of cerebral amyloid in vivo with a monoclonal antibody
- PMID: 8021711
- PMCID: PMC9887729
- DOI: 10.1097/00005072-199407000-00009
Labeling of cerebral amyloid in vivo with a monoclonal antibody
Abstract
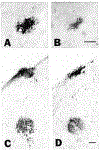
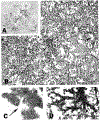
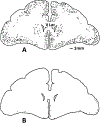
We assessed the ability of a murine monoclonal antibody to bind selectively to beta-amyloid in the brains of living nonhuman primates. To circumvent the blood-brain barrier, we injected unlabeled antibody 10D5 (murine whole IgG1 and/or Fab fragments) into the cerebrospinal fluid of the cisterna magna in three aged monkeys. A control animal was given an intracisternal injection of nonimmune mouse whole IgG plus Fab. Twenty-four hours later, the animals were perfused and prepared for immunohistochemical detection of bound murine immunoglobulin in brain. All three experimental animals showed selective binding of 10D5 to approximately 5-15% of amyloid deposits in cerebral cortex, primarily near the cortical surface. There was no labeling in the control animal. In vivo-labeled deposits were confirmed to be beta-amyloid by electron microscopy and by in vitro immunohistochemistry in adjacent sections. The animals tolerated the injection well, although some polymorphonuclear leukocytes infiltrated portions of the subarachnoid space and superficial neocortex. These results provide the first demonstration that it may be feasible to selectively direct a tagged monoclonal antibody to beta-amyloid in the brain for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes. With enhancement of labeling efficiency, the method also may be useful for studying the progression of beta-amyloidosis in experimental animals using emission tomography.
Figures


References
-
- Glenner GG, Wong CW. Alzheimer's disease: Initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1984; 120:885–890 - PubMed
-
- Kemper T. Neuroanatomical and neuropathological changes in normal aging and in dementia. In: Albert ML, ed. Clinical Neurology of Aging. New York: Oxford University Press, 1984: 9–52
-
- Mandybur TI. Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: The vascular pathology and complications. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 1986; 45:79–90 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

