The effects of weight loss by exercise or by dieting on plasma high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels in men with low, intermediate, and normal-to-high HDL at baseline
- PMID: 8028519
- PMCID: PMC2864614
- DOI: 10.1016/0026-0495(94)90277-1
The effects of weight loss by exercise or by dieting on plasma high-density lipoprotein (HDL) levels in men with low, intermediate, and normal-to-high HDL at baseline
Abstract
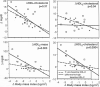
To assess whether baseline plasma high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol levels affected the HDL response to weight loss, we examined lipoprotein changes in overweight men aged 30 to 59 years who were randomized to lose weight by exercise training (primarily running, n = 46) or by caloric restriction (ie, dieting, n = 42) or to remain sedentary, nondieting controls (n = 42) in a 1-year study. In exercisers, absolute increases in HDL (mg/dL) were greatest in men with normal-to-high baseline HDL and least in men with low baseline HDL. Specifically, when divided into groups of low (< or = 37 mg/dL), intermediate (38 to 47 mg/dL), and normal-to-high HDL cholesterol (> or = 48 mg/dL) at baseline, the exercisers increased HDL cholesterol by 2.3 +/- 1.9, 4.9 +/- 1.1, and 7.0 +/- 1.3 mg/dL, respectively; HDL2 cholesterol by 0.8 +/- 1.6, 2.3 +/- 1.2, and 5.1 +/- 1.3 mg/dL; and HDL2 mass by 2.8 +/- 5.1, 9.5 +/- 8.9, and 31.7 +/- 11.0 mg/dL. Relative increases in HDL cholesterol were more similar in the low (7.1% +/- 6.1%), intermediate (12.4% +/- 3.9%), and normal-to-high men (13.2% +/- 4.0%). Regression analyses were performed to assess whether baseline HDL cholesterol was related to the amount of absolute HDL change per unit of weight loss. In exercisers, the increase in HDL3 cholesterol concentrations was significantly greater in men with low HDL than in those with normal-to-high HDL at entry (2.0 +/- 0.8 v 0.2 +/- 0.8 mg/dL per kg/m2 lost).(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Figures


References
-
- Miller GJ, Miller NE. Plasma high density lipoprotein concentrations and the development of ischaemic heart disease. Lancet. 1975;1:16–19. - PubMed
-
- Stampfer MJ, Sacks FM, Salvinis S, et al. A prospective study of cholesterol, apolipoproteins and risk of myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 1991;315:373–381. - PubMed
-
- National Cholesterol Education Program Report of the Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. Washington DC: US Department of Health and Human Services. Public Health Services, National Institutes of Health. US Government Printing Office 234-6211/00222; p. 78.
-
- Wood PD, Stefanick ML, Dreon D, et al. Changes in plasma lipid and lipoproteins in overweight men during weight loss through dieting as compared with exercise. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:1173–1179. - PubMed
-
- Williams PT, Krauss RM, Vranizan KM, et al. Changes in lipoprotein subfractions during diet-induced and exercise-induced weight loss in moderately overweight men. Circulation. 1990;81:1293–1314. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

