A "slow" homotetrameric kinesin-related motor protein purified from Drosophila embryos
- PMID: 8083185
- PMCID: PMC3201834
A "slow" homotetrameric kinesin-related motor protein purified from Drosophila embryos
Abstract
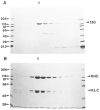
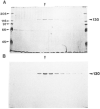
Pan-kinesin peptide antibodies (Cole, D. G., Cande, W. Z., Baskin, R. J., Skoufias, D. A., Hogan, C. J., and Scholey, J. M. (1992) J. Cell Sci. 101, 291-301; Sawin, K. E., Mitchinson, T. J., and Wordeman, L. G. (1992) J. Cell Sci. 101, 303-313) were used to identify and isolate kinesin-related proteins (KRPs) from Drosophila melanogaster embryonic cytosol. These KRPs cosedimented with microtubules (MTs) polymerized from cytosol treated with AMP-PNP (adenyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate), and one of them, KRP130, was further purified from ATP eluates of the embryonic MTs. Purified KRP130 behaves as a homotetrameric complex composed of four 130-kDa polypeptide subunits which displays a "slow" plus-end directed motor activity capable of moving single MTs at 0.04 +/- 0.01 microns/s. The 130-kDa subunit of KRP130 was tested for reactivity with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies that are specific for various members of the kinesin superfamily. Results indicate that the KRP130 subunit is related to Xenopus Eg5 (Sawin, K. E., Le Guellec, K. L., Philippe, M., Mitchinson, T. J. (1992) Nature 359, 540-543), a member of the BimC subfamily of kinesins. Therefore, KRP130 appears to be the first Drosophila KRP, and the first member of the BimC subfamily in any organism, to be purified from native tissue as a multimeric motor complex.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

