Expression of extracellular ligand-binding domain of murine guanylate cyclase/atrial natriuretic factor receptor cDNA in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 8094955
- PMCID: PMC6027598
- DOI: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1109
Expression of extracellular ligand-binding domain of murine guanylate cyclase/atrial natriuretic factor receptor cDNA in Escherichia coli
Abstract
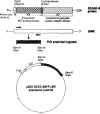
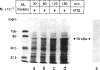
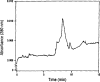
The membrane-bound form of guanylate cyclase/atrial natriuretic factor receptor (GC/ANF-R) is a 135 kDa transmembrane glycoprotein which binds ANF with high affinity. We have expressed the extracellular ligand-binding domain of murine guanylate cyclase ANF-R (GC/ANFR-LBD) cDNA in Escherichia coli. The cDNA encoding the extracellular ANF-binding domain (nucleotide positions covering from 432-1755 base pair) of GC/ANF-R was amplified by polymerase chain reaction, cloned into BamHI site of pGEX-3X prokaryotic expression vector and was transfected into E. coli, strain JM101. After isopropyl-beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) induction of bacterial cells, the GC/ANFR-LBD was expressed as the glutathione-S-transferase (GST) fusion protein, yielding a molecular mass of 70 kDa. The expressed fusion protein was characterized for binding affinity to both full length and truncated ANF molecules. After expression in E. coli, the binding of 125I-ANF to the extracellular region of GC/ANF-R was similar and corresponded to the pharmacological class of native receptor protein. The 70 kDa fusion product was purified as a predominant single protein band by glutathione-affinity chromatography. These findings establish that E. coli may be utilized as an effective heterologous model system to delineate the structure-function analysis of guanylate cyclase-coupled ANF receptor molecules.
Figures


References
-
- de Bold AJ, Borenstein HB, Veress AT, Sonnenberg H. Life Sei. 1981;28:89–94. - PubMed
-
- de Bold AJ. Science. 1985;230:767–770. - PubMed
-
- Cantin M, Genest J. Endocrine Rev. 1985;6:107–127. - PubMed
-
- Inagami T. J Biol Chem. 1989;264:3043–3046. - PubMed
-
- Rosenzweig A, Seidman CE. Ann Rev Biochem. 1991;60:229–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

