Cholinergic mechanisms in startle and prepulse inhibition: effects of the false cholinergic precursor N-aminodeanol
- PMID: 8097917
- PMCID: PMC9170527
- DOI: 10.1037//0735-7044.107.2.306
Cholinergic mechanisms in startle and prepulse inhibition: effects of the false cholinergic precursor N-aminodeanol
Abstract
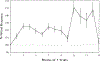
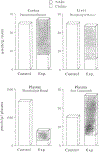
We examined the effects of cholinergic deficiency on prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustic startle. Rats treated with a choline-free diet that contained the false cholinergic precursor N-aminodeanol showed great deficit in PPI. This deficit does not appear to be secondary to an increase of stereotyped behaviors. Startle threshold was also greatly reduced, as these rats startled to the 70-dB prepulse and the baseline startle amplitude was increased by 60% over the control rats. Arecoline (4 mg/kg) partially reversed the deficit in PPI. This improvement persisted beyond the period of drug treatment. On the other hand, scopolamine (1 mg/kg) reduced PPI in the control rats. These results suggest that cholinergic systems play a major role in both the elicitation and prepulse inhibition of startle.
Figures
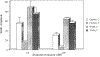




References
-
- Caine SB, Geyer MA, & Swerdlow NR (1991). Carbachol infusion into the dentate gyrus disrupts sensorimotor gating of startle in the rat. Psychopharmacology, 105, 347–354. - PubMed
-
- Carlton PL (1964). Brain acetylcholine and habituation. In Bradley PB & Finks M. (Eds.), Progress in brain research (Vol. 18, pp 48–60). New York: Elsevier. - PubMed
-
- Carlton PL (1969). Brain—Acetylcholine and inhibition. In Tapp JR (Ed.), Reinforcement and behavior (pp. 286–327). San Diego: Academic Press.
-
- Crofton KM, Dean KF, Sheets LP, & Peele D. (1990). Evidence for an involvement of associative conditioning in reflex modification of the acoustic startle response with gaps in background noise. Psychobiology, 8, 467–474.
-
- Crofton KM„ Sheets LP, Dean KF„ & Peele DB (1988). The effects of experience on gap inhibition of the acoustic startle response (ASR). Society for Neuroscience Abstracts, 4, 60.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

