Primary structure effects on peptide group hydrogen exchange
- PMID: 8234246
- PMCID: PMC3438223
- DOI: 10.1002/prot.340170110
Primary structure effects on peptide group hydrogen exchange
Abstract
The rate of exchange of peptide group NH hydrogens with the hydrogens of aqueous solvent is sensitive to neighboring side chains. To evaluate the effects of protein side chains, all 20 naturally occurring amino acids were studied using dipeptide models. Both inductive and steric blocking effects are apparent. The additivity of nearest-neighbor blocking and inductive effects was tested in oligo- and polypeptides and, surprisingly, confirmed. Reference rates for alanine-containing peptides were determined and effects of temperature considered. These results provide the information necessary to evaluate measured protein NH to ND exchange rates by comparing them with rates to be expected for the same amino acid sequence is unstructured oligo- and polypeptides. The application of this approach to protein studies is discussed.
Figures
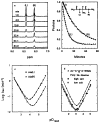
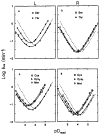
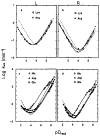
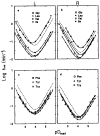
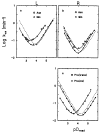


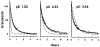
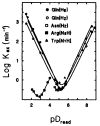
References
-
- Englander SW, Kallenbach NR. Hydrogen exchange and structural dynamics of proteins and nucleic-acids. Q Rev Biophys. 1984;16:521–655. - PubMed
-
- Berger A, Loewenstein A, Meiboom S. NMR study of the protolysis and ionization of N-methylacetamide. J Am Chem Soc. 1959;81:61–67.
-
- Englander JJ, Calhoun DB, Englander SW. Measurement and calibration of peptide group hydrogen-deuterium exchange by ultraviolet spectrophotometry. Anal Biochem. 1979;92:517–524. - PubMed
-
- Gregory RB, Crabo L, Percy AJ, Rosenberg A. Water catalysis of peptide hydrogen isotope exchange. Biochemistry. 1983;22:910–917. - PubMed
-
- Englander SW, Poulsen A. Hydrogen-tritium exchange of the random chain polypeptide. Biopolymers. 1969;7:329–339.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

