A case of primary intestinal lymphangiectasia
- PMID: 8268148
- PMCID: PMC4532082
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.1993.8.1.51
A case of primary intestinal lymphangiectasia
Abstract
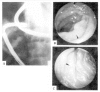
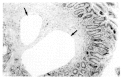
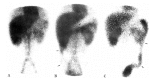
A 26-year-old male patient who had an 8 years history of recurrent peripheral edema with diarrhea and hypoproteinemia was evaluated. Endoscopic jejunal and ileal biopsy revealed markedly dilated mucosal lymph vessels with no evidence of inflammation. 99mTc-labeled human serum albumin (HSA) scintigraphy showed significant activity accumulating in the gastrointestinal tract to represent 99mTc-HSA leakage into the bowel lumen. A diagnosis of protein losing enteropathy and intestinal lymphangiectasia could be made. After treatment with a high protein and fat restricted diet, his symptoms subsided and the serum protein level was normalized.
Figures
References
-
- Waldmann TA, Stein JL, Dutcher TF, Davidson RS, Gordon TR. The role of the gastrointestinal system in “Idiopathic hypoproteinemia”. Gastroenterology. 1961;41:197. - PubMed
-
- Holman H, Nickel WF, Jr, Sleisenger MH. Hypoproteinemia antedating intestinal lesions and possibly due to excessive serum protein loss into the intestine. Am J Med. 1959;27:963. - PubMed
-
- Mistilis SP, Skyring AP, Stephen DD. Intestinal lymphangiectasia. Mechanism of enteric loss of plasma-protein and fat. Lancet. 1965;1:77. - PubMed
-
- Divigi CR, Lisaun NM, Yeh SDJ, Benua RS. Technetium 99mTc-albumin scintigraphy in the diagnosis of protein-losing enteropathy. J Nucl Med. 1986;27:1710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
