Detection of shared MHC-restricted human melanoma antigens after vaccinia virus-mediated transduction of genes coding for HLA
- PMID: 8335937
- PMCID: PMC2121328
Detection of shared MHC-restricted human melanoma antigens after vaccinia virus-mediated transduction of genes coding for HLA
Abstract
To detect shared human melanoma Ag that are recognized by HLA-A2 restricted, melanoma-specific CTL derived from tumor infiltrating lymphocytes, we have developed a convenient method to insert and express foreign HLA genes capable of presenting Ag on target cell lines. Seventeen melanoma cell lines and 11 nonmelanoma cell lines were infected with recombinant vaccinia virus containing the HLA-A2.1 gene. Infection by the vaccinia virus resulted in expression of functional HLA-A2 molecules on the cell surface of virtually 100% of infected cells within a 3.5-h period. The results showed that 11 of 17 (65%) naturally HLA-A2- melanoma cell lines were specifically lysed by the HLA-A2-restricted, melanoma-specific TIL after infection with the vaccinia-HLA-A2.1 virus. None of the nine human nonmelanoma cell lines tested (three colon cancer, four breast cancer, or two immortalized non-tumor cell lines) or two murine melanoma cell lines were lysed by the HLA-A2-restricted TIL after vaccinia-HLA-A2.1 infection. Coinfection of the vaccinia virus containing the beta 2-microglobulin gene with the vaccinia-HLA-A2.1 virus increased the surface expression of HLA-A2 and subsequent lysis by melanoma-specific tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. With this new method we could extend previous findings demonstrating that shared melanoma Ag recognized by HLA-A2-restricted tumor infiltrating lymphocytes exist among melanoma cells from different patients regardless of HLA type. These Ag represent excellent candidates for the development of vaccines to induce T cell responses for the immunotherapy of patients with melanoma.
Figures
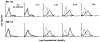
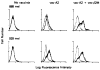
References
-
- Rosenberg SA, Speiss P, Lafreniere RA. New approach to the adoptive immunotherapy of cancer with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. Science. 1986;233:1318. - PubMed
-
- Barth RJ, Bock SN, Mulé JJ, Rosenberg SA. Unique murine tumor-associated antigens identified by tumor infiltrating lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1990;144:1531. - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg SA, Packard BS, Aebersold PM, Solomon D, Topalian SL, Toy ST, Simon P, Lotze MT, Yang JC, Seipp CA, Simpson C, Carter C, Bock S, Schwartzentruber D, Wei JP, White DE. Use of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes and interleukin 2 in the immunotherapy of patients with metastatic melanoma: preliminary report. N Engl J Med. 1988;319:1676. - PubMed
-
- Topalian SL, Solomonm D, Rosenberg SA. Tumor specific cytolysis by lymphocytes infiltrating human melanomas. J Immunol. 1989;142:3714. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
