Beta-endorphin is a potent inhibitor of thymidine incorporation into DNA via mu- and kappa-opioid receptors in fetal rat brain cell aggregates in culture
- PMID: 8380443
- PMCID: PMC2571952
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03214.x
Beta-endorphin is a potent inhibitor of thymidine incorporation into DNA via mu- and kappa-opioid receptors in fetal rat brain cell aggregates in culture
Abstract
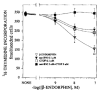
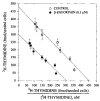
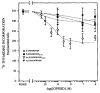
Thymidine incorporation into DNA was inhibited dose-dependently by beta-endorphin in rat fetal brain cell aggregate cultures. The inhibition was reversed partially by mu (cyclic D-Phe-Cys-Tyr-D-Trp-Orn-Thr- Pen-Thr amide) or kappa (norbinaltorphimine) antagonists. Complete blockade of the beta-endorphin inhibitory effect was achieved only on concomitant exposure to both antagonists. Eadie-Hofstee analysis revealed that beta-endorphin inhibited thymidine incorporation noncompetitively. In the presence of protease inhibitors, beta-endorphin decreased thymidine incorporation with an IC50 of 0.7 nM. Truncated and N-acetylated beta-endorphin derivatives, which bind with low affinity to opioid receptors, did not affect thymidine incorporation. These findings indicate that beta-endorphin at physiological concentrations can regulate thymidine incorporation in cultured brain cells.
Figures
References
-
- Akil H, Young E, Watson SJ. Opiate binding properties of naturally occurring N- and C-terminus modified β-endorphins. Peptides. 1981;2:289–292. - PubMed
-
- Barg J, Levy R, Simantov R. Expression of the three opioid receptor subtypes μ, δ and κ in guinea pig and rat brain cell cultures and in vivo. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1989;7:173–179. - PubMed
-
- Barg J, Belcheva MM, Bern WT, Lambourne B, McLachlan JA, Tolman KC, Johnson FE, Coscia CJ. Desipramine modulation of sigma and opioid peptide receptor expression in glial cells. Peptides. 1991;12:845–849. - PubMed
-
- Barg J, Rius RA, Bern WT, Belcheva MM, Loh YP, Coscia CJ. Differential development of β-endorphin and μ opioid binding sites in mouse brain. Dev Brain Res. 1992a;66:71–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

