kappa-Opioid agonist modulation of [3H]thymidine incorporation into DNA: evidence for the involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein-coupled phosphoinositide turnover
- PMID: 8384252
- PMCID: PMC2586989
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03314.x
kappa-Opioid agonist modulation of [3H]thymidine incorporation into DNA: evidence for the involvement of pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein-coupled phosphoinositide turnover
Abstract
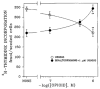
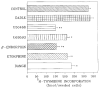
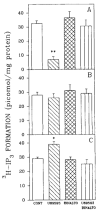
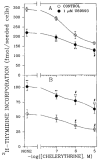
A body of evidence has indicated that mu-opioid agonists can inhibit DNA synthesis in developing brain. We now report that kappa-selective opioid agonists (U69593 and U50488) modulate [3H]thymidine incorporation into DNA in fetal rat brain cell aggregates in a dose- and developmental stage-dependent manner, kappa agonists decreased thymidine incorporation by 35% in cultures grown for 7 days, and this process was reversed by the kappa-selective antagonist, norbinaltorphimine, whereas in 21-day brain cell aggregates a 3.5-fold increase was evident. Cell labeling by [3H]thymidine was also inhibited by the kappa-opioid agonist as shown by autoradiography. In addition, U69593 reduced basal rates of phosphoinositide formation in 7-day cultures and elevated it in 21-day cultures. Control levels were restored by norbinaltorphimine. Pertussis toxin blocked U69593-mediated inhibition of DNA synthesis. The action of kappa agonists on thymidine incorporation in the presence of chelerythrine, a protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor, or in combination with LiCl, a noncompetitive inhibitor of inositol phosphatase, was attenuated in both 7- and 21-day cultures. These results suggest that kappa agonists may inhibit DNA synthesis via the phosphoinositide system with a pertussis toxin-sensitive G protein as transducer. In mixed glial cell aggregates, U50488 increased thymidine incorporation into DNA 3.1-fold, and this stimulation was reversed by the opioid antagonist naltrexone.
Figures




References
-
- Ashkenazi A, Ramachandran J, Capon DJ. Acetylcholine analogue stimulates DNA synthesis in brain-derived cells via specific muscarinic receptor subtypes. Nature. 1989;340:146–150. - PubMed
-
- Attali B, Gouarderes V, Mazarguil H, Cros J. Evidence for multiple kappa binding sites by use of opioid peptides in the guinea pig lumbosacral spinal cord. Neuropeptides. 1982;3:53–64. - PubMed
-
- Attali B, Nah SY, Vogel Z. Phorbol ester pretreatment desensitizes the inhibition of Ca2+ channels induced by κ-opiate, α2-adrenergic, and muscarinic receptor agonists. J Neurochem. 1991;57:1803–1806. - PubMed
-
- Barg J, Levy R, Simantov RJ. Paradoxical and subtype-specific effects of opiate antagonists on the expression of opioid receptors in rat brain cultures. J Neurosci Res. 1989a;22:322–330. - PubMed
-
- Barg J, Levy R, Simantov R. Expression of the three opioid receptor subtypes μ, δ, and κ in guinea pig and rat brain cell cultures and in vivo. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1989b;7:173–180. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

