Pathophysiology of massive infantile spasms: perspective on the putative role of the brain adrenal axis
- PMID: 8388675
- PMCID: PMC3786774
- DOI: 10.1002/ana.410330302
Pathophysiology of massive infantile spasms: perspective on the putative role of the brain adrenal axis
Abstract
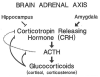
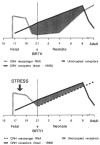
Massive infantile spasms are an age-specific seizure syndrome of infancy. Uniquely, the spasms respond to hormonal manipulation using adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) or glucocorticoids. A hypothesis explaining the efficacy of hormonal therapy, age-specificity, multiple causative factors, and spontaneous resolution of infantile spasms is presented. Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), an excitant neuropeptide suppressed by ACTH/steroids, is implicated. Evidence for the age-specific convulsant properties of CRH is presented, and a putative scenario in which a stress-induced enhancement of endogenous CRH-mediated seizures is discussed. Clinical testing of the CRH-excess theory and its therapeutic implications are suggested.
Figures
References
-
- Aicardi J, Aicardi J. Epilepsy in children. Raven Press; New York: 1986. Infantile spasms and related syndromes; pp. 17–38.
-
- Kellaway P, Frost JD, Hrachovy RA, Morselli PL, Pippenger CG, Penry JK. Antiepileptic drug therapy in pediatrics. Raven Press; New York: 1983. Infantile spasms; pp. 115–136.
-
- Jeavons PM, Bower BD. Infantile spasms. Clin Dev Med. 1964;15:1–82.
-
- Holmes GL. Diagnosis and management of seizures in children. WB Saunders; Philadelphia: 1987. pp. 212–225.
-
- Bellman M, Pedley TA, Meldrum BS. Recent advances in epileptology. Churchill-Livingstone; Edinburgh: 1983. Infantile spasms; pp. 113–138.

