Clonal analysis of a human antibody response. II. Sequences of the VH genes of human IgM, IgG, and IgA to rabies virus reveal preferential utilization of VHIII segments and somatic hypermutation
- PMID: 8432980
- PMCID: PMC4667541
Clonal analysis of a human antibody response. II. Sequences of the VH genes of human IgM, IgG, and IgA to rabies virus reveal preferential utilization of VHIII segments and somatic hypermutation
Abstract
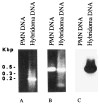
The construction of mAb-producing cell lines has been instrumental in dissecting the fine specificities and genetic makeup of murine antibodies to exogenous and self Ag. The analysis of the genetic composition of human antibody responses has been hampered by the difficulty in generating human mAb of predetermined class and specificity. Using B lymphocytes from three healthy subjects vaccinated with inactivated rabies virus vaccine, we generated nine human mAb binding to rabies virus and analyzed the genes encoding their VH regions. Six mAb (five IgG1 and one IgA1) were monoreactive and displayed high affinities for rabies virus Ag. The remaining three mAb (IgM) were polyreactive and displayed lower affinities for rabies virus Ag. Seven mAb (3 IgG1, the IgA1, and the three IgM) utilized VH gene segments of the VHIII family. The remaining two IgG1 mAb utilized gene segments of the VHI and VHIV families. Of the seven expressed VHIII family genes, three were similar to the germline VH26c gene, two to the germline 22-2B gene, one to the germline H11 gene, and one to the germline 8-1B gene. The expressed VHI and VHIV genes displayed sequences similar to those of the germline hv1263 and V71-4 genes, respectively. The VH genes of all but one mAb (mAb55) resembled those that are predominantly expressed by C mu + clones in human fetal liver libraries. When compared with known germline sequences, the VH genes of the rabies virus-binding mAb displayed variable numbers of nucleotide differences. That such differences resulted from a process of somatic hypermutation was formally demonstrated (by analyzing DNA from polymorphonuclear neutrophil of the same subject whose B lymphocytes were used for the mAb generation) in the case of the VH gene of the high affinity (anti-rabies virus glycoprotein) IgG1 mAb57 that has been shown to efficiently neutralize the virus in vitro and in vivo. The distribution, mainly within the complementarity determining regions, and the high replacement-to-silent ratio of the mutations, were consistent with the hypothesis that the mAb57-producing cell clone underwent a process of Ag-driven affinity maturation through clonal selection. The D gene segments of the rabies virus-selected mAb were heterogeneous and, in most cases, flanked by significant N segment additions. The JH segment utilization was unbalanced and reminiscent of those of the adult and fetus. Four mAb utilized JH4, two JH6, two JH3, and one JH5; no mAb utilized JH1 or JH2 genes.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Figures



References
-
- Berek C, Milstein C. Mutation drift and repertoire shift in the maturation of the immune response. Immunol Rev. 1987;96:23. - PubMed
-
- Apel M, Berek C. Somatic mutations in antibodies expressed by germinal centre B cells early after primary immunization. Int Immunol. 1990;2:813. - PubMed
-
- Malipiero UV, Levy NS, Gearhart PJ. Somatic mutation in anti-phosphorylcholine antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1987;96:59. - PubMed
-
- Claflin JL, Berry J, Flaherty D, Dunnick W. Somatic evolution of diversity among anti-phosphocholine antibodies induced with Proteus morganii. J Immunol. 1987;138:3060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
