cGMP-dependent protein kinase in dorsal root ganglion: relationship with nitric oxide synthase and nociceptive neurons
- PMID: 8627352
- PMCID: PMC6579134
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-10-03130.1996
cGMP-dependent protein kinase in dorsal root ganglion: relationship with nitric oxide synthase and nociceptive neurons
Abstract
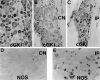
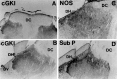
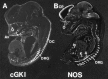
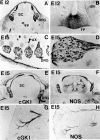
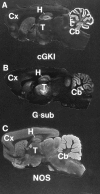
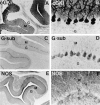
Nitric oxide and cGMP influence plasticity of nociceptive processing in spinal cord. However, effectors for cGMP have not been identified in sensory pathways. We now demonstrate that cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (cGKl) occurs in the DRGs at levels comparable to that in cerebellum, the richest source of cGKl in the body. Immunohistochemical studies reveal that cGKl is concentrated in a subpopulation of small- and medium-diameter DRG neurons that partially overlap with substance P and calcitonin gene-related polypeptide containing cells. During development, cGKl expression throughout the embryo is essentially restricted to sensory neurons and to the spinal floor and roof plates. Neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) is coexpressed with cGKl in sensory neurons during embryonic development and after peripheral nerve axotomy. The primary target for cGKl in cerebellum, G-substrate, is not present in developing, mature, or regenerating sensory neurons, indicating that other proteins serve as effectors for cGKl in sensory processing. These data establish sensory neurons as a primary locus for cGMP actions during development and suggest a role for cGKl in plasticity of nociception.
Figures



References
-
- Aanonsen LM, Wilcox GL. Nociceptive action of excitatory amino acids in the mouse: effects of spinally administered opioids, phencyclidine and sigma agonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987;243:9–19. - PubMed
-
- Aimi Y, Fujimura M, Vincent SR, Kimura H. Localization of NADPH-diaphorase-containing neurons in sensory ganglia of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1991;306:382–392. - PubMed
-
- Arancio O, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD. Activity-dependent long-term enhancement of transmitter release by presynaptic 3′,5′-cyclic GMP in cultured hippocampal neurons. Nature. 1995;376:74–80. - PubMed
-
- Aswad DW, Greengard P. A specific substrate from rabbit cerebellum for guanosine 3′:5′-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. I. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981;256:3487–3493. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
