A macromolecular synthesis-dependent late phase of long-term potentiation requiring cAMP in the medial perforant pathway of rat hippocampal slices
- PMID: 8627357
- PMCID: PMC6579127
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-10-03189.1996
A macromolecular synthesis-dependent late phase of long-term potentiation requiring cAMP in the medial perforant pathway of rat hippocampal slices
Abstract
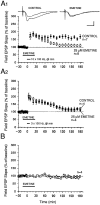
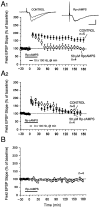
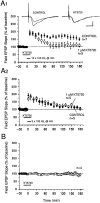
Memory storage consists of a short-term phase that is independent of new protein synthesis and a long-term phase that requires the synthesis of new proteins and RNA. A cellular representation of these two phases has been demonstrated recently for long-term potentiation (LTP) in both the Schaffer collateral and the mossy fibers of the hippocampus, a structure widely thought to contribute to memory consolidation. By contrast, much less information is available about the medial perforant pathway (MPP), one of the major inputs to the hippocampus. We found that both a short-lasting and a long-lasting potentiation (L-LTP) can be induced in the MPP of rat hippocampal slices by applying repeated tetanization in reduced levels of magnesium. This potentiation was dependent on the activation of NMDA receptors. The early, transient phase of LTP in the MPP did not require either protein or RNA synthesis, and it was independent of protein kinase A activation. By contrast, L-LTP required the synthesis of proteins and RNA, and was selectively blocked by inhibitors of cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA). Forskolin, an adenylate cyclase activator, also induced a L-LTP that was attenuated by inhibition of transcription. Our results demonstrate that, like LTP in the Schaffer collateral and mossy fiber pathways, MPP LTP also consists of a late phase that is dependent on protein and RNA synthesis and PKA activity. Thus, cAMP-mediated transcription appears to be a common mechanism for the late form of LTP in all three pathways within the hippocampus.
Figures




References
-
- Abraham WC, Mason SE, Demoner J, Williams JM, Richardson CL, Tate WP, Lawlor PA, Dragunow M. Correlations between immediate early gene induction and persistence of LTP. Neuroscience. 1993;56:717–727. - PubMed
-
- Alberini CM, Ghirardi M, Metz R, Kandel ER. C/EBP is an immediate-early gene required for the consolidation of long-term facilitation in Aplysia . Cell. 1994;85:1099–1114. - PubMed
-
- Amaral DG. Emerging principles of intrinsic hippocampal organization. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993;3:225–229. - PubMed
-
- Andersen P, Bliss TVP, Skrede KK. Lamellar organization of hippocampal excitatory pathways. Exp Brain Res. 1971;13:222–238. - PubMed
-
- Andersen P, Sundberg SH, Sven O, Wigström H. Specific long-lasting potentiation of synaptic transmission in hippocampal slices. Nature. 1977;266:736–737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
