Multiple structural elements determine subunit specificity of Mg2+ block in NMDA receptor channels
- PMID: 8642401
- PMCID: PMC6578835
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-11-03549.1996
Multiple structural elements determine subunit specificity of Mg2+ block in NMDA receptor channels
Abstract
In NMDA receptor channels, subtype-specific differences of Mg2+ block are determined by the NR2 subunits. Channels assembled from the NR1-NR2A or NR1-NR2B subunits are blocked more strongly than channels formed by the NR1-NR2C or NR1-NR2D subunits, predominantly reflecting a difference in voltage dependence. A determinant of Mg2+ block common to the NR2 subunits is located in the M2 domain (N-site or Q/R/N-site). However, subunit-specific differences of block suggested that additional structural elements exist. Chimeric NR2 subunits were constructed by replacing segments of the least sensitive NR2C subunit with homologous segments of the most sensitive NR2B subunit. Mutant NR2 subunits were coexpressed with wild-type NR1 in Xenopus oocytes, and Mg2+ block was quantified. Replacement of the entire M1-M4 region resulted in a chimera with a sensitivity of Mg2+ block similar to that of the NR2B wild type. Replacing smaller segments or introducing point mutations did not generate channels with Mg2+ block characteristic of NR2B wild type. However, combining in a single chimera three small segments (M1, M2-M3 linker, M4), each independently mediating an increase in Mg2+ block, produced channels close to NR2B wild type. Thus, differences in Mg2+ block as controlled by the NR2 subunits cannot be explained by a single structural determinant in addition to the N-site. Moreover, three elements of the NR2 subunit are the major determinants of subtype-specific differences of Mg2+ block in heteromeric NMDA receptor channels.
Figures

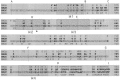
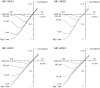
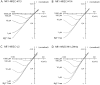
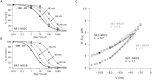
Similar articles
-
Adjacent asparagines in the NR2-subunit of the NMDA receptor channel control the voltage-dependent block by extracellular Mg2+.J Physiol. 1998 Jan 1;506 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):13-32. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.013bx.x. J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9481670 Free PMC article.
-
Mg2+ and memantine block of rat recombinant NMDA receptors containing chimeric NR2A/2D subunits expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes.J Physiol. 2008 Jan 1;586(1):211-25. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.143164. Epub 2007 Oct 25. J Physiol. 2008. PMID: 17962329 Free PMC article.
-
Internal Mg2+ block of recombinant NMDA channels mutated within the selectivity filter and expressed in Xenopus oocytes.J Physiol. 1998 Feb 15;507 ( Pt 1)(Pt 1):1-12. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.001bu.x. J Physiol. 1998. PMID: 9490808 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol sensitivity of NMDA receptors.Neurochem Int. 2002 Dec;41(6):377-82. doi: 10.1016/s0197-0186(02)00046-3. Neurochem Int. 2002. PMID: 12213224 Review.
-
N-{2-[4-(4-[125I]Iodobenzyl)-piperidin-1-ylmethyl]benzoimidazol-5-yl}-methanesulfonamide.2011 Jan 31 [updated 2011 Mar 31]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. 2011 Jan 31 [updated 2011 Mar 31]. In: Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): National Center for Biotechnology Information (US); 2004–2013. PMID: 21473036 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanistic and structural determinants of NMDA receptor voltage-dependent gating and slow Mg2+ unblock.J Neurosci. 2013 Feb 27;33(9):4140-50. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3712-12.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23447622 Free PMC article.
-
Cocaine Experience Enhances Thalamo-Accumbens N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Function.Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Nov 1;80(9):671-681. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.04.002. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27209241 Free PMC article.
-
Ionic flow enhances low-affinity binding: a revised mechanistic view into Mg2+ block of NMDA receptors.J Physiol. 2010 Feb 15;588(Pt 4):633-50. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.178913. Epub 2009 Dec 21. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20026615 Free PMC article.
-
Stoichiometry of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors within the suprachiasmatic nucleus.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Jun;103(6):3448-64. doi: 10.1152/jn.01069.2009. Epub 2010 Apr 21. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20410362 Free PMC article.
-
Going the Extra (Synaptic) Mile: Excitotoxicity as the Road Toward Neurodegenerative Diseases.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Apr 24;14:90. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.00090. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32390802 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akazawa C, Shigemoto R, Bessho Y, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N. Differential expression of five N -methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit mRNAs in the cerebellum of developing and adult rats. J Comp Neurol. 1994;347:150–160. - PubMed
-
- Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (1995) Mutagenesis of cloned DNA. In: Current protocols in molecular biology, Chap 8. (Janssen K, ed). New York: Wiley.
-
- Bennett JA, Dingledine R. Topology profile for a glutamate receptor: three transmembrane domains and a channel-lining reentrant membrane loop. Neuron. 1995;14:373–384. - PubMed
-
- Bliss TVP, Collingridge GL. A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature. 1993;361:31–39. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
