The taste of monosodium glutamate: membrane receptors in taste buds
- PMID: 8656276
- PMCID: PMC6578609
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.16-12-03817.1996
The taste of monosodium glutamate: membrane receptors in taste buds
Abstract
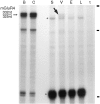
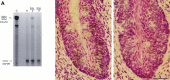
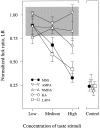
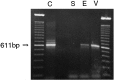
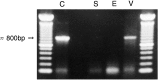
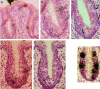
Receptor proteins for photoreception have been studied for several decades. More recently, putative receptors for olfaction have been isolated and characterized. In contrast, no receptors for taste have been identified yet by molecular cloning. This report describes experiments aimed at identifying a receptor responsible for the taste of monosodium glutamate (MSG). Using reverse transcriptase (RT)-PCR, we found that several ionotropic glutamate receptors are present in rat lingual tissues. However, these receptors also could be detected in lingual tissue devoid of taste buds. On the other hand, RT-PCR and RNase protection assays indicated that a G-protein-coupled metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR4, also is expressed in lingual tissues and is limited only to taste buds. In situ hybridization demonstrated that mGluR4 is detectable in 40-70% of vallate and foliate taste buds but not in surrounding nonsensory epithelium, confirming the localization of this metabotropic receptor to gustatory cells. Expression of mGluR4 in taste buds is higher in preweaning rats compared with adult rats. This may correspond to the known higher sensitivity to the taste of MSG in juvenile rodents. Finally, behavioral studies have indicated that MSG and L-2-amino-4-phosphonobutyrate (L-AP4), a ligand for mGluR4, elicit similar tastes in rats. We conclude that mGluR4 may be a chemosensory receptor responsible, in part, for the taste of MSG.
Figures
References
-
- Abe T, Sugihara H, Nawa H, Shigemoto R, Mizuno N, Nakanishi S. Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca2+ signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:13361–13368. - PubMed
-
- Abe K, Kusakabe Y, Tanemura K, Emori Y, Arai S. Primary structure and cell-type specific expression of a gustatory G protein-coupled receptor related to olfactory receptors. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:12033–12039. - PubMed
-
- Akabas MH. The molecular biology of chemotransduction. In: Simon SA, Roper SD, editors. Mechanisms of taste transduction. CRC; Boca Raton, FL: 1993. pp. 175–200.
-
- Akabas MH, Dodd J, Al-Awqati Q. A bitter substance induces a rise in intracellular calcium in a sub-population of rat taste cells. Science. 1988;242:1047–1050. - PubMed
-
- Avenet P, Hofmann F, Lindemann B. Transduction in taste receptor cells requires cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1988;331:51–54. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
